Fig. 6.
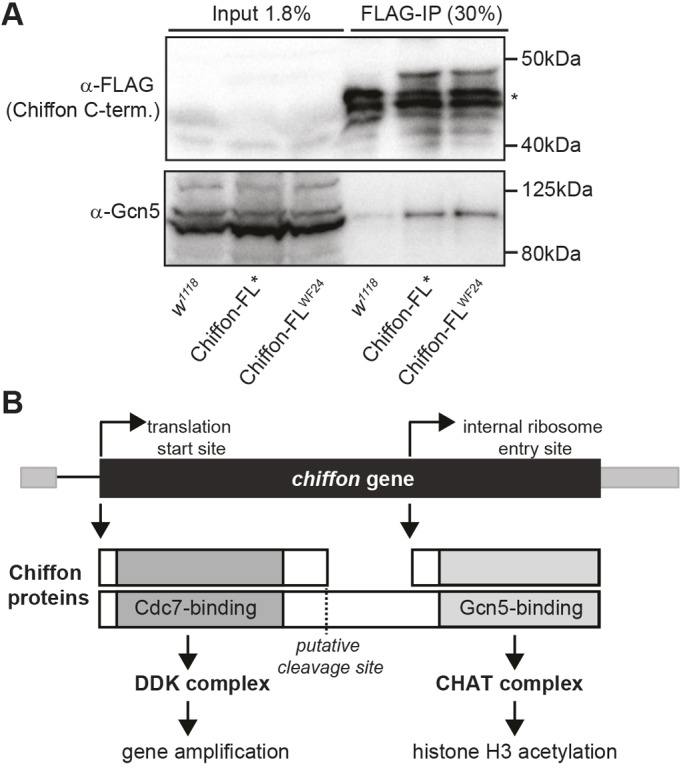
An internal translation start site in chiffon expresses a C-terminal product that binds Gcn5. (A) C-terminally FLAG-tagged Chiffon-FL* or Chiffon-FLWF24 transgenes, that contain premature stop codons at amino acids 376 or 174, respectively, were immunoprecipitated from embryo lysates using anti-FLAG antibodies. Co-immunoprecipitated proteins were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and western blotting with antibodies against FLAG (Chiffon) and Gcn5. The asterisk indicates nonspecific bands present in the w1118 control. Representative data from three experiments are shown. (B) Schematic illustrating the two polypeptides encoded by chiffon. The first start codon encodes full-length Chiffon (1695 aa) with the conserved Dbf4 Cdc7-binding domain in its N-terminal region. The N-terminal Chiffon product binds Cdc7, nucleates DDK formation and is necessary for gene amplification. An alternative internal ribosome entry site generates a C-terminal product containing the insect-specific Gcn5-binding domain that nucleates CHAT formation, and is essential for histone acetylation and development. Our data suggest that two mechanisms might control production of the alternative Chiffon products that nucleate DDK versus CHAT complex formation: (1) translational switching between cap-dependent and IRES-dependent start sites; and/or (2) proteolytic cleavage of full-length Chiffon.
