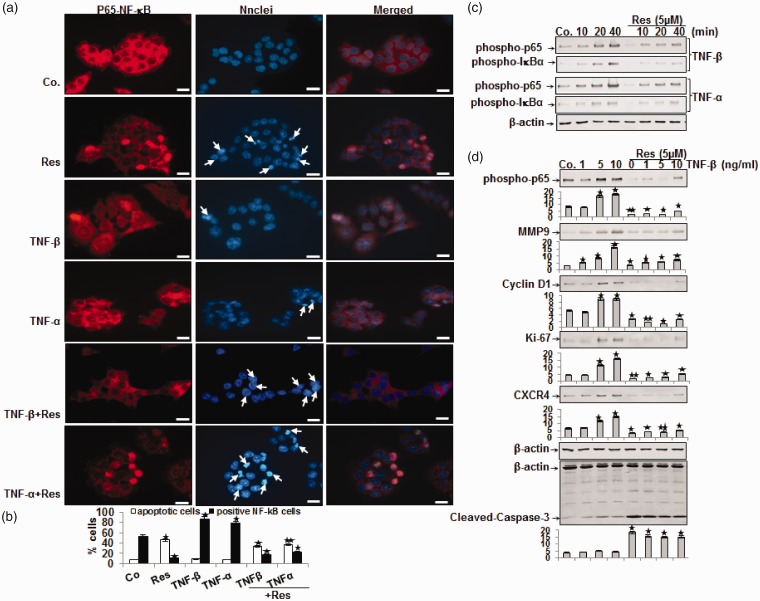
Figure 4.
Effect of resveratrol on 10 ng/mL TNF-β- or TNF-α-induced activation and nuclear translocation of p65 and NF-κB-regulated gene end-products in HCT116 cells. (a) HCT116 cells in monolayer culture were treated as described in Materials and Methods, labeled for p65 by immunofluorescence and counterstained with DAPI. The white arrows indicate apoptotic cells. Magnification 600×; bar = 30 µm. (b) Percentage of positively stained cells and apoptotic nuclei was quantified by counting 800–1000 cells from 10 different microscopic fields and values were compared to the control and statistically significant values with P < 0.05 are designated by an (*); P < 0.01 by two (**). Number of NF-κB-/apoptotic-positive cells was significantly lower/higher in the resveratrol+TNF groups than in the TNF groups. (c) Time- and (d) dose-dependent experiments of HCT116 cells in monolayer culture were performed as described in Materials and Methods. Immunoblotting of whole cell lysates was performed for anti-phospho-p65, anti-phospho-IκBα, anti-MMP-9, anti-cyclin D1, anti-Ki-67, anti-CXCR4, and anti-cleaved-caspase-3. The results are shown from at least three independent experiments and the housekeeping protein β-actin served as an internal loading control. Densitometric evaluation was performed for phospho-p65, MMP-9, cyclin D1, Ki-67, CXCR4 and cleaved-caspase-3. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.