Figure 9. The abnormality of glutamate metabolism and disturbed water homeostasis in the early phase of ischemic injury following HI onset are affected by pretreatment with Ginseng or DMF in an Nrf2-dependent manner.
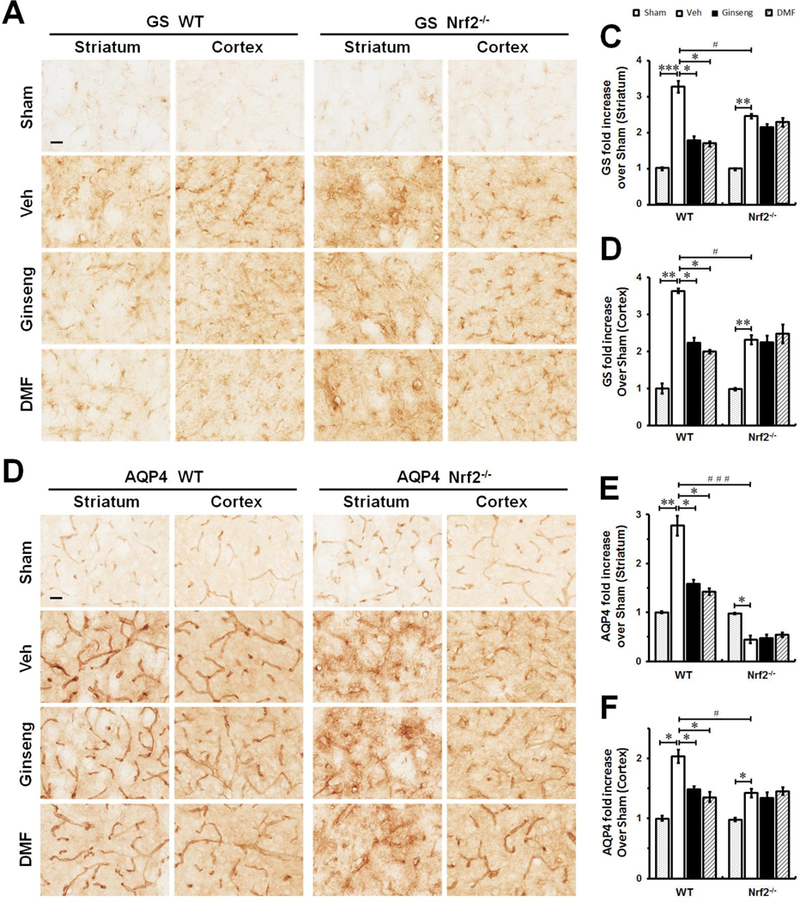
The representative images of GS (A) and AQP4 (B) in the ipsilateral striatum and cortex of mice at 24 h after HI; and open squares in top left image indicate the peri-infarct areas of striatum and cortex used for micrographic examination. Scare bar: 50 μm. Quantifications of GS signals (C and D) of A and AQP4 signals (E and F) of B. In the initial phase of ischemic injury, pretreatment with Ginseng or DMF significantly attenuated the rapid increase of GS and AQP4 expressions in both brain regions in WT mice, but not in Nrf2−/− mice. In contrast, Nrf2 deficiency displayed significant lower expression levels in GS and AQP4 signals compared to WT controls. Interestingly, in response to initial ischemic insult, Nrf2−/− mice underwent quick decline in AQP4 expression in striatum but not cortex compared to WT controls. n = 4–6 per group. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, #P < 0.05, ###P < 0.001.
