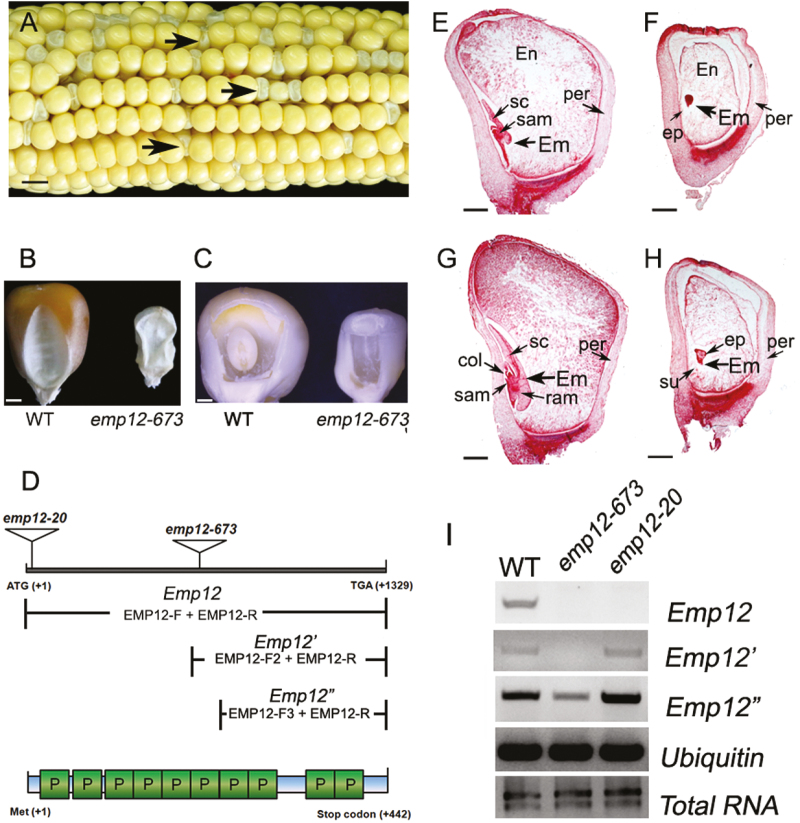
Fig. 1.
The maize Emp12 gene is involved in embryogenesis and endosperm development. (A) A self-pollinated ear segregating for emp12-673 mutant kernels at 15 days after pollination (DAP). Arrows show the emp maize kernels. Scale bar=0.5 cm. (B) The dried kernels of emp12-673 mutants and the wild type (WT). Scale bar=2 mm. (C) The embryo and endosperm of emp12-673 mutant and WT kernels at 12 DAP. Arrows indicate the embryo (Em). Scale bar=2 mm. (D) Schematic diagram of the Emp12 gene and its protein structure, showing the Mu insertion sites of emp12-673 and emp12-20. The expression of full-length and partial Emp12 (Emp12' and Emp12'') downstream of the insertion sites was detected by RT–PCR analysis, with the combinations of primers EMP12-F, EMP12-F2, EMP12-F3, and EMP12-R. PPR motifs (P) of EMP12 are predicted by TPRpred (https://toolkit.tuebingen.mpg.de/#/tools/tprpred). (E–H) Light microscopy of cytological sections of WT (E, G) and emp12-673 mutant kernels (F, H) are longitudinally sectioned early at 12 DAP (E, F) and late at 16 DAP (G, H). En, endosperm; Em, embryo; per, pericarp; sc, scutellum; su, suspensor; col, coleoptile; ep, embryo proper; sam, shoot apical meristem; ram, root apical meristem. Scale bar=1 mm. (I) RT–PCR analysis of full-length Emp12 and truncated Emp12' and Emp12'' expression indicated in (D) was performed in the emp12-673 and emp12-20 mutants and WT siblings at 12 DAP, with normalization by Ubiquitin primers.