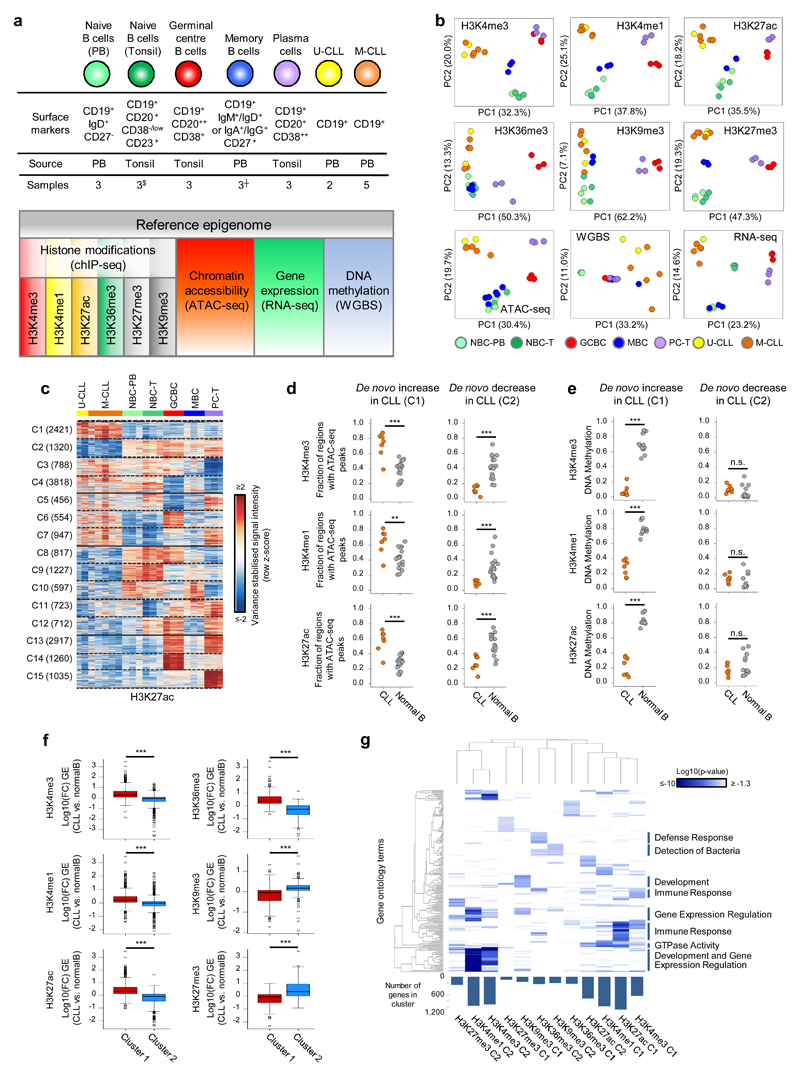
Fig. 1. CLL reference epigenomes.
(a) Overview of analyzed CLL and normal B-cell samples (upper panel) for the nine layers of the reference epigenome (lower panel). $no whole-genome bisulfite sequencing data available; ┼six instead of three biologically independent samples analyzed for chromatin accessibility. (b) Unsupervised principal component analysis for the nine layers of the reference epigenome. Number of datapoints analyzed to generate the PCAs: H3K4me3 (n=38,499 independent genomic regions), H3K4me1 (n=37,871 independent genomic regions), H3K27ac (n=47,191 independent genomic regions), H3K36me3 (n=15,561 independent genomic regions), H3K9me3 (n=27,371 independent genomic regions), H3K27me3 (n=12,878 independent genomic regions), ATAC-seq (n=91,671 independent genomic regions), WGBS (n=15,825,190 independent CpGs), RNA-seq (n=36,190 independent genes). Sample sizes were for U-CLL: n=2 biologically independent samples (all nine layers), for M-CLL: n=5 biologically independent samples (all nine layers), for NBC-PB, GCBC and PC-T: n=3 biologically independent samples (all nine layers), for NBC-T: n=3 biologically independent samples (all layers except WGBS that does not include NBC-T), for MBC: n=3 biologically independent samples (all layers except ATAC-seq for which 6 biologically independent samples were used). (c) K-means clustering of independent genomic regions showing differences in the dynamics of H3K27ac levels in CLL and normal B cells. For each cluster (C1-C15) the number of independent genomic regions is indicated in brackets. C1 and C2 respectively represent regions with de novo increase and de novo decrease in CLL. (d) Fraction of regions in CLL (n=7 biologically independent samples) and normal B cells (n=15 biologically independent samples) harboring ATAC-seq peaks in regions with de novo increase (C1) or de novo decrease (C2) in CLL of H3K4me3 (respective P-values 5.5 x 10-4 and 4.2 x 10-6), H3K4me1 (respective P-values 6.1 x 10-3 and 2.9 x 10-5) and H3K27ac (respective P-values 5.5 x 10-4 and 1.9 x 10-4). P-values were calculated using a Wilcoxon rank sum test (two-sided). (e) Median DNA methylation levels in CLL (n=7 biologically independent samples) and normal B cells (n=15 biologically independent samples) of regions with de novo increase (C1) or de novo decrease (C2) in CLL of H3K4me3 (respective P-values 4.5 x 10-4 and 1.6 x 10-1), H3K4me1 (respective P-values 4.5 x 10-4 and 1.6 x 10-1) and H3K27ac (respective P-values 4.5 x 10-4 and 4.2 x 10-1). P-values were calculated using a Wilcoxon rank sum test (two-sided). (f) Boxplots of log10 transformed fold changes (FC) in gene expression (GE) levels in CLL versus normal B cells of all genes located within regions with de novo increase (cluster 1, C1) or de novo decrease (cluster 2, C2) in CLL. For each gene the mean log10 transformed GE levels of CLL (n=7 biologically independent samples) and normal B cells (n=15 biologically independent samples) were calculated and subtracted to obtain the log10 transformed FC between CLL and normal B cells. H3K4me3 (P-value 8.2 x 10-77, mean, minimum, 25th, 50th and 75th percentile and maximum log10(FC) and number of datapoints (= independent genes) C1: 0.43, -1.85, 0.09, 0.29, 0.65, 3.47, 624 and C2: -0.15, -3.62, -0.33, -0.04, 0.10, 1.41, 911), H3K4me1 (P-value 3.9 x 10-50, mean, minimum, 25th, 50th and 75th percentile and maximum log10(FC) and number of datapoints (= independent genes) C1: 0.29, -1.42, 0.05, 0.21, 0.49, 3.47, 971 and C2: -0.05, -2.09, -0.23, -0.02, 0.10, 2.27, 952), H3K27ac (P-value 5.3 x 10-137, mean, minimum, 25th, 50th and 75th percentile and maximum log10(FC) and number of datapoints (= independent genes) C1: 0.44, -1.05, 0.12, 0.32, 0.64, 3.47, 1,081 and C2: -0.25, -2.42, -0.46, -0.09, 0.09, 1.63, 713), H3K36me3 (P-value 1.1 x 10-52, mean, minimum, 25th, 50th and 75th percentile and maximum log10(FC) and number of datapoints (= independent genes) C1: 0.52, -0.65, 0.19, 0.34, 0.72, 3.47, 233 and C2: -0.37, -2.32, -0.68, -0.26, 0.01, 1.13, 235), H3K9me3 (P-value 3.3 x 10-10, mean, minimum, 25th, 50th and 75th percentile and maximum log10(FC) and number of datapoints (= independent genes) C1: -0.16, -1.73, -0.44, -0.04, 0.07, 1.32, 160 and C2: 0.16, -1.91, 0.06, 0.17, 0.30, 1.74, 206) and H3K27me3 (P-value 3.0 x 10-17, mean, minimum, 25th, 50th and 75th percentile and maximum log10(FC) and number of datapoints (= independent genes) C1: -0.22, -2.32, -0.51, -0.06, 0.12, 0.98, 92 and C2: 0.52, -0.93, 0.00, 0.35, 0.93, 3.47, 262). P-values were calculated using a Student's t-test (two-sided). (g) Heatmap of p-values of gene ontology (GO) terms (rows, n= 190 independent GO terms, only the top 20 terms per cluster were included) that were significantly enriched (p-value < 0.05) among the genes overlapping with regions with de novo increase (C1) or de novo decrease (C2) of the six histone marks in CLL. The GO term enrichment and significance were calculated per cluster separately. The number of independent genes per cluster used in this calculation is indicated below the heatmap, their exact numbers were: H3K4me3 (C1: 624, C2: 911), H3K4me1 (C1: 971, C2: 952), H3K27ac (C1: 1,081, C2: 713), H3K36me3 (C1: 233, C2: 235), H3K9me3 (C1: 160, C2: 206) and H3K27me3 (C1: 92, C2: 262). U-CLL, CLL with unmutated IGHV; M-CLL, CLL with mutated IGHV; NBC-PB, naive B cell from peripheral blood; NBC-T, naive B cell from tonsil; GCBC, germinal centre B cell; MBC, memory B cell; PC-T, plasma cell from tonsil; GE, gene expression.