Figure 1. Biotin biosynthesis pathway.
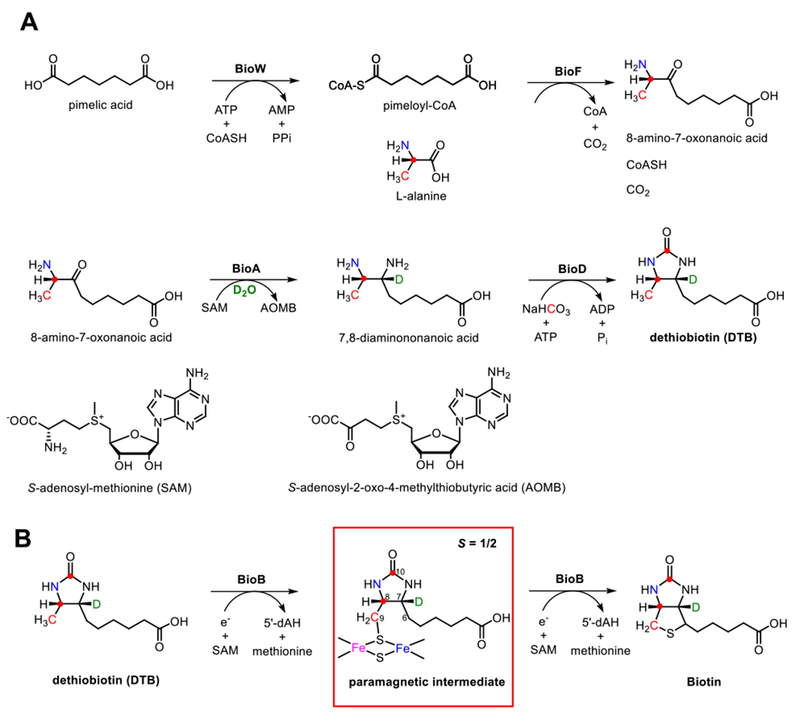
A, Biosynthesis of DTB from exogenous pimelic acid requires BioW, BioF, BioA and BioD enzymes along with appropriate substrate and cofactors; this pathway was exploited for in vitro biosynthesis of isotopically labeled DTB. In E. coli, pimeloyl acyl carrier protein is generated de novo by BioC, BioH, and fatty acid synthase and likely serves as a direct substrate for BioF. B, In the final step of biotin biosynthesis, the radical SAM enzyme BioB catalyzes the formation of biotin via two sequential hydrogen-atom abstractions from the substrate DTB leading to the sulfur incorporation. Isotopically-labeled nuclei investigated in this work are shown in color.
