Figure 5.
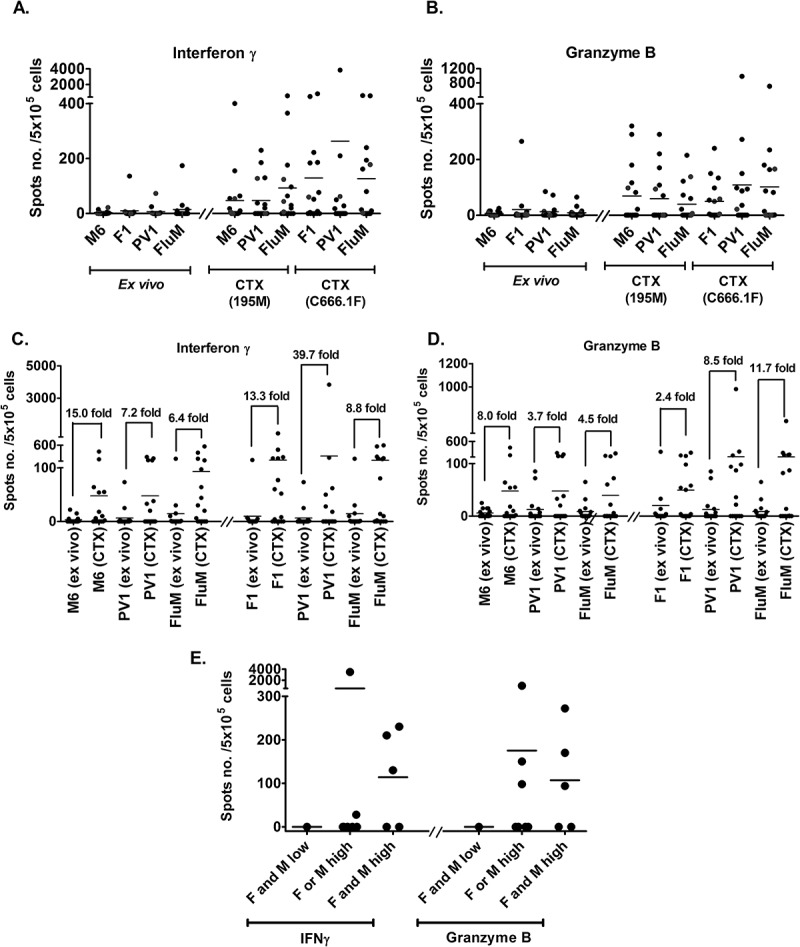
In vitro stimulation with PV1 peptides increases cytokine secretion in PMBC obtained from HNSCC patients (n = 16).
The graphs show the: (A) IFNγ and (B) granzyme B secretion from PBMC of patients in the ex vivo and cytotoxic (CTX) ELISPOT assays. Prior to peptide vaccine stimulation (ex vivo), inherent T-cell response against M6, F1 and PV1 is low. The level of cytokine secretion increased after the T-cells were stimulated by peptide-pulsed DCs (CTX). Ex vivo assays were conducted by exposing PBMCs to peptides in overnight cultures and measuring the response. In the CTX assay, T cells were co-cultured with autologous peptide-pulsed DC and expanded with IL-2 prior to incubation with the respective target cell lines in overnight cultures. Fold change increment of: (C) IFNγ and (D) granzyme B secreting T-cell post M6, F1, PV1 and FluM peptides stimulation is shown. (E) Patients were placed into 3 groups based on the intensity of MAGED4B and FJX1 staining of their tumour tissues. Patients with high expression of MAGED4B/FJX1 in their tumours have better responses when stimulated with PV1, and secrete higher levels of IFNγ and granzyme B in the cytotoxic ELISPOT assay, compared to patients with low expression of these proteins. 195M cells were used as target cells for T cells stimulated with MAGED4B peptide and C666.1F was used for T cells stimulated with FJX1 peptide.
