Fig. 3.
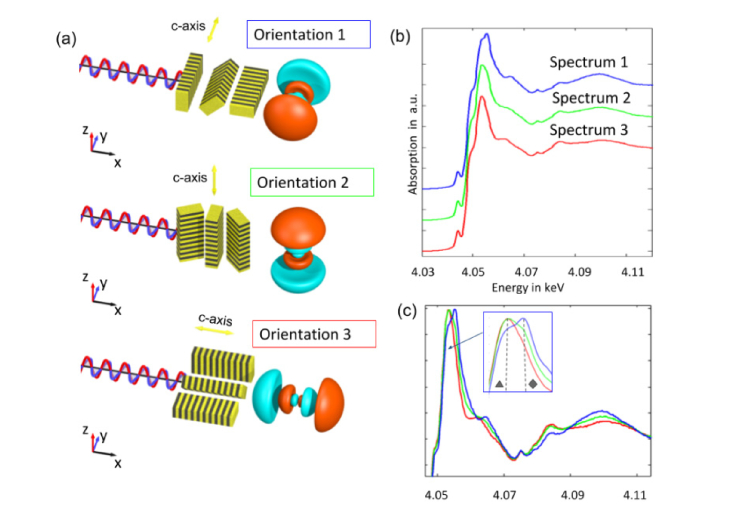
Polarisation effects in XANES spectroscopy at the Ca K-edge of tooth c-HAP: a) Schematic drawing of three orientations of the c-HAP crystals and the 4p3/2 orbital of Ca relative to the polarisation (along y-axis). Depending on crystal orientation with respect to the polarization axis, the interactions vary due to an angular absorption dependence. The 3D crystal orientation can be determined by sample rotation around the illumination axis. b) The XANES spectra corresponding to the three orientations shown in (a) were normalized at the edge and shifted vertically with an offset for clarity. c) Same spectra as (b) normalised to the maximum. The three spectra differ mainly in the main absorption (so called white line) region due to 1s to 4p transitions. The energies of E1 = 4.0533keV and E2 = 4.0553keV correspond to the 1s to 4p1/2 (marked ▲) and 1s to 4p3/2 (marked ♦) dipole transitions, respectively. In orientation 1, polarization is parallel to the c-HAP crystal c-axis and the 4p3/2 orbital where the probability of 1s to 4p3/2 transition is higher. In orientation 2 and 3, polarization is perpendicular to the crystals c-axis, where the probability of 1s to 4p1/2 transitions is higher.