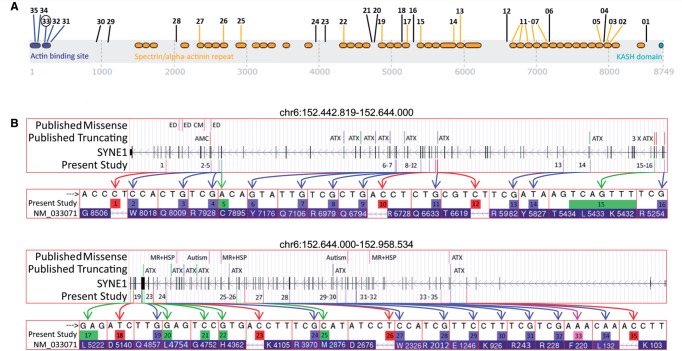
Figure 1.
SYNE1 mutations . ( A ) Graphical overview of the mutations found in this study in relation to the SYNE1 domains. Numbers indicate the mutation IDs of the mutations identified in this study ( Table 1 ). Their position indicates the position of the respective mutations in the SYNE1 gene. Blue = N-terminal actin binding domain [calponin homology domains containing actin binding sites (IPR001715)] and mutations affecting this domain; orange = spectrin/alpha-actinin repeat domains (IPR018159) and mutations affecting these domains; turquoise = KASH domain (C-terminal klarsicht domain) (IPR012315); black = mutations not affecting any of these domains. Mutation 33 (black circle) is the only missense mutation in the present study. ( B ) Overview of the variant types and their location of all published and novel SYNE1 mutations. The presentation of the giant SYNE1 gene is split in a first part (chr6:152.442.819–152.644.000; top ) and a second part (chr6:152.644.000–152.958.534; bottom ). It presents the variant types of all SYNE1 mutations found in the present study ( bottom row of each panel) and other studies (Human Gene Mutation Database) ( top row of each panel), their location and their annotation with the associated clinical phenotypes. ATX = ataxia; AMC = arthrogryposis multiplex congenita; ED = Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy; CM = cardiomyopathy; MR = mental retardation; HSP = hereditary spastic paraplegia. Note that, except for ATX and AMC, all other phenotypes have been associated only with missense mutations, not truncating mutations in SYNE1 . Green coloured arrows and boxes = indel mutations; blue coloured arrows and boxes = stop mutations; red coloured arrows and boxes = splice site mutations; purple coloured arrow and box = missense mutation. HG19 genome build. Transcript: NM_033071 > NP_149062.