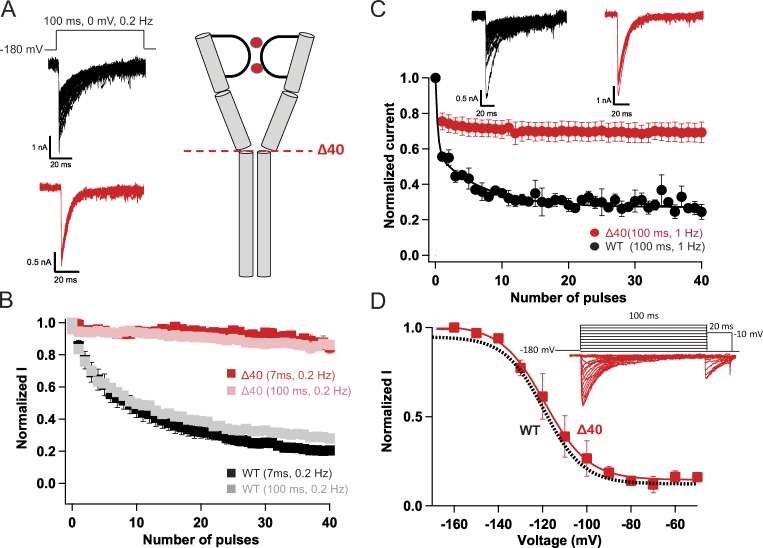
Figure 4.
Truncation of the C-terminal tail abolishes late use-dependent inactivation. (A) Representative current traces showing late use-dependent inactivation of NaVAb WT (black) and loss of late use-dependent inactivation in NaVAbΔ40 (red). (B) Peak inward currents recorded during each pulse in trains of depolarizations at 0.2 Hz and normalized to the current produced by the first depolarization of the train for NaVAbΔ40 (7 ms, red, n = 7; 100 ms, pink, n = 5) and NaVAb/WT (7 ms, black, n = 7; 100 ms, gray n = 11). (C) Top: Representative currents recorded during each pulse in trains of depolarizations at 1 Hz. Bottom: Normalized currents during each depolarizing pulse for NaVAbΔ40 (red, n = 3) and NaVAb/WT (black, n = 5). (D) Top: Representative currents for NaVAb40 (red) during 100-ms conditioning pulses followed by 20-ms test pulses. Bottom: Voltage dependence of inactivation for NaVAb40 (red) compared with NaVAb/WT (black), as reported previously (Lenaeus et al., 2017). Error bars represent SEM.