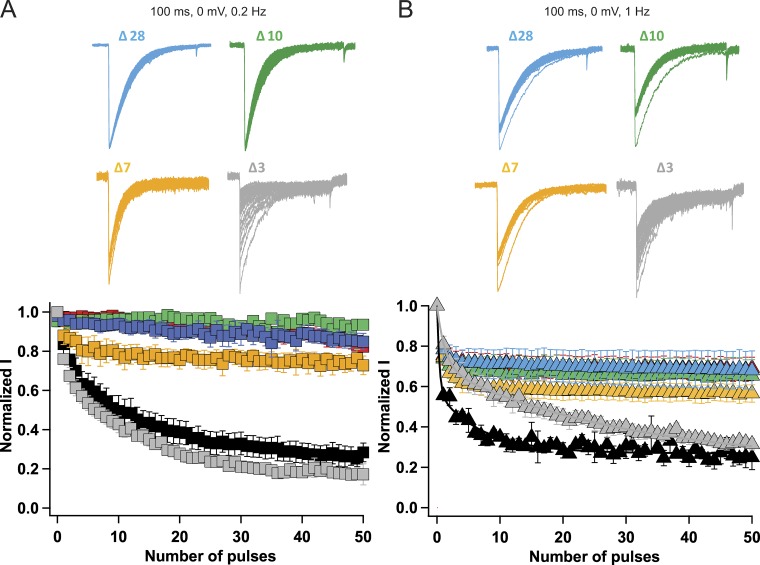
Figure 5.
Graded effects of C-terminal tail truncations on late use-dependent inactivation. (A) Top: Current traces elicited by applying 100-ms depolarizing pulses from a holding potential of −180 mV to 0 mV at 0.2 Hz for different truncated constructs. Bottom: Peak inward currents measured during each train of pulses and normalized to the current produced by the first depolarization of the train for NaVAb/WT (black, n = 7), NaVAb 40 (red, n = 7), NaVAb 28 (blue, n = 12), NaVAb 10 (green, n = 5), NaVAb 7 (yellow, n = 9), and NaVAb 3 (gray, n = 5). (B) Top: Current traces elicited by 100-ms depolarizations from a holding potential of −180 mV at 1 Hz with different constructs. Bottom: Use-dependent inactivation profile of the different constructs during application of 100-ms repetitive pulses applied at 1 Hz. NaVAb WT (black, n = 7), NaVAbΔ40 (red, n = 11), NaVAbΔ28 (blue, n = 6), NaVAbΔ10 (green, n = 5), NaVAbΔ7 (yellow, n = 6), and NaVAbΔ3 (gray, n = 5). Error bars represent SEM.