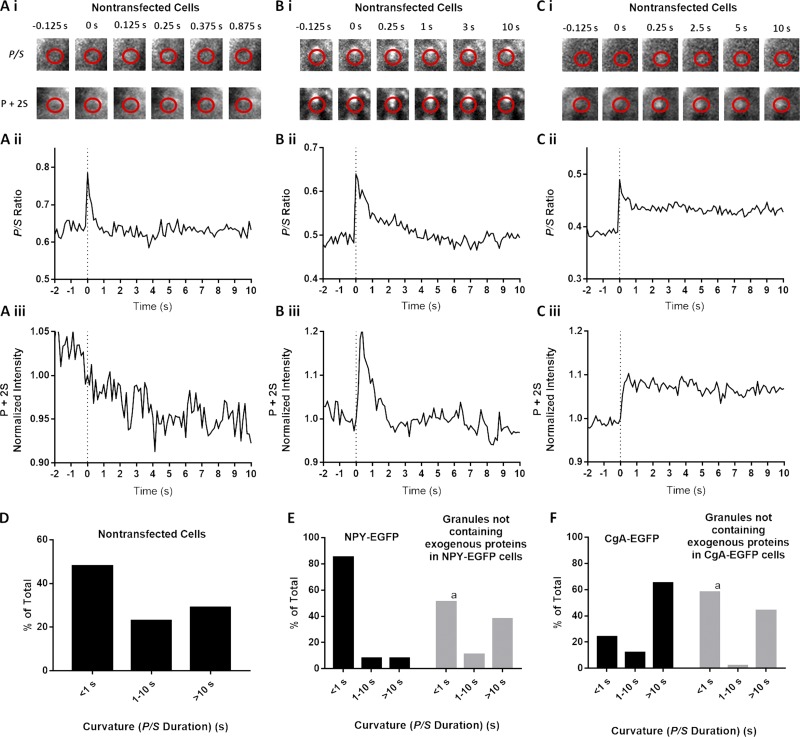
Figure 8.
Expression of exogenous lumenal protein alters fusion pore lifetimes. (A–C) Chromaffin cells were transfected to express NPY-EGFP or CgA-EGFP or used without transfection. Transfected and nontransfected cells were stained with DiI, stimulated with elevated K+, and imaged using pTIRF. In nontransfected cells stained with DiI, discrete, punctate changes in fluorescence became visible after stimulation with elevated K+. Three events detected by pTIRF microscopy in nontransfected cells are shown in A, B, and C. (D) P/S lifetimes for events in nontransfected cells (n = 135). (E and F) In transfected cells, granules expressing exogenous protein were identified by EGFP fluorescence, and their discharge and fusion pore expansion were monitored using pTIRF. In the same cells, fusion of granules without transfected protein (i.e., without fluorescent EGFP) was identified as discrete, punctate changes in DiI fluorescence that became visible after stimulation. P/S in the different groups were binned according to their durations. n = 78 NPY-EGFP–expressing granules, n = 37 granules without transfected protein in NPY-EGFP–transfected cells, n = 34 CgA-EGFP–expressing granules, n = 54 granules without transfected protein in CgA-EGFP–transfected cells. A χ2 test was performed to compare the distributions. a, significant difference between distribution of curvature durations of granules without transfected protein compared with NPY-EGFP–containing (P < 0.0001) or CgA-EGFP–containing (P = 0.0051) granules.