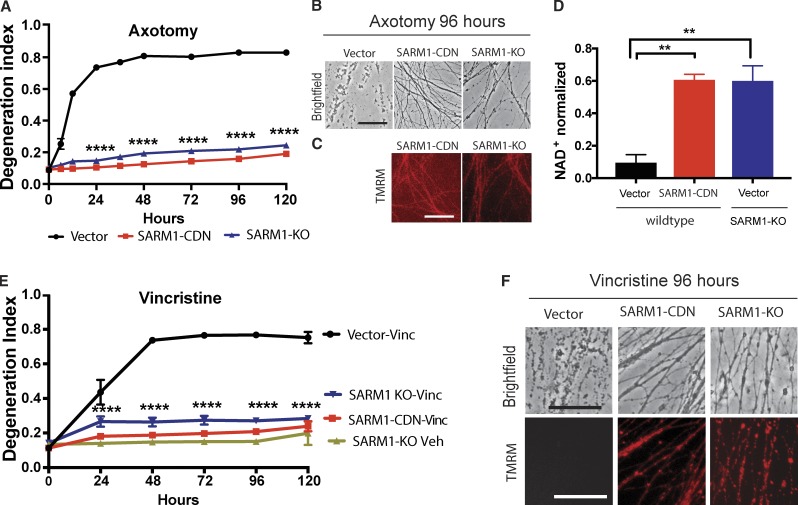
Figure 2.
SARM1-CDN potently inhibits wild-type SARM1 function. (A) Degeneration of wild-type DRG neurons expressing EGFP vector or the SARM1-CDN and of SARM1 KO neurons expressing EGFP vector after transection. DI ranges from 0 (completely intact) to 1 (completely fragmented). Data are presented as mean ± SEM, tested with a two-way ANOVA, which shows significant main effects of group F(2,9) = 2,710, P < 0.0001; time (F8,72) = 298.7, P < 0.0001, and interaction F(16,72) = 154, P < 0.0001. Dunnett’s multiple comparison test vector versus SARM1-CDN and SARM1-KO, ****, P = 0.0001. (B and C) Representative brightfield (B) and TMRM (C) images of axons expressing constructs indicated in A, at 96 h after axotomy. (D) HPLC was used to measure NAD+ levels in wild-type and SARM1-KO neurons expressing EGFP vector or SARM1-CDN from axon extracts 4 h after transection and normalized to baseline (immediately after cut). A one-way ANOVA shows a significant main effect F(2,6) = 20.01, P = 0.0022; post hoc Tukey’s multiple comparison test shows vector versus SARM1-CDN, **, P = 0.0036; vector versus SARM1-KO, **, P = 0.0039; SARM1-KO versus SARM1-CDN, P = 0.9969. n = 3 independent experiments. (E) Wild-type DRG neurons expressing EGFP vector or SARM1-CDN and SARM1-KO neurons were treated with 40 nM vincristine or vehicle and AxD determined using the DI. Data are represented as means ± SEM; two-way ANOVA shows significant main effect of groups F(3,8) = 259.6; P < 0.0001; time F(5,40) = 89.28, P < 0.0001; and interaction F(15,40) = 38.59; P < 0.0001; post hoc Dunnett’s multiple comparison test shows wild-type vector vincristine versus SARM1-CDN vincristine, SARM1-KO vincristine, and SARM1-KO vehicle, ****, P = 0.0001; n = 3 independent experiments. (F) Representative brightfield (top row) and TMRM (bottom row) images of the constructs indicated in D, at 96 h after vincristine administration. Bars, 50 µm.