Figure 3.
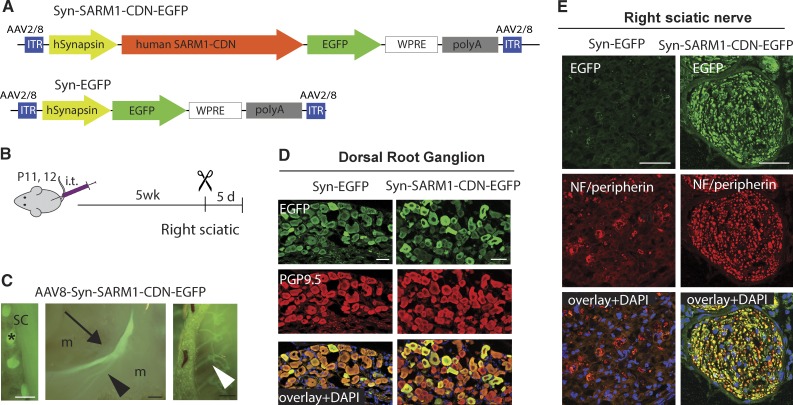
SARM1-CDN efficiently transduces DRGs in vivo and protects from AxD. (A) Top: Schematic of the AAV vector expressing human SARM1-CDN under control of the neuron-specific human synapsin promoter (Syn-SARM1-CDN-EGFP). Bottom: Schematic of the EGFP vector (Syn-EGFP) used for control experiments. WPRE, woodchuck hepatitis virus posttranscriptional regulatory element; ITR, inverted terminal repeats. (B) AAV8-Syn-SARM1-CDN-EGFP or EGFP vector (AAV8-Syn-EGFP) were injected intrathecally (i.t.) into mice at postnatal day 11 or 12 (P11/12). 5 wk later, the right sciatic nerve was transected, and 5 d later, tissue was collected for analysis. (C) Representative micrographs taken in situ of (from left to right) DRGs (asterisk) attached to the spinal cord (SC), the left (uninjured) sciatic nerve (arrow) with its branches (arrowheads), and intercostal nerves (white arrowhead) expressing GFP 5.5 wk after injection with AAV8-Syn-SARM1-CDN-EGFP; m, muscle. Bars, 2 mm. (D) Representative confocal image of a 6-µm-thick section of a DRG after injecting EGFP vector (left column; Syn-EGFP) or SARM1-CDN (right column; Syn-SARM1-DN-EGFP). Sections were stained with PGP9.5 (red; DRG neurons) and anti-GFP (green; construct expression) and coverslipped with Vectamount containing DAPI (blue; nuclear marker). (E) Representative confocal image of a 6-µm-thick section of the right (transected) sciatic nerve taken 5 d after cut in mice injected with the EGFP vector (left column; Syn-EGFP) or SARM1-CDN (right column; Syn-SARM1-CDN-EGFP). Sections were stained with antibodies to Neurofilament 200 (NF) and peripherin (red; axonal markers) and green fluorescent protein (green; construct expression) and mounted with Vectashield containing DAPI (blue; nuclear marker). Bars, 50 µm (D and E).