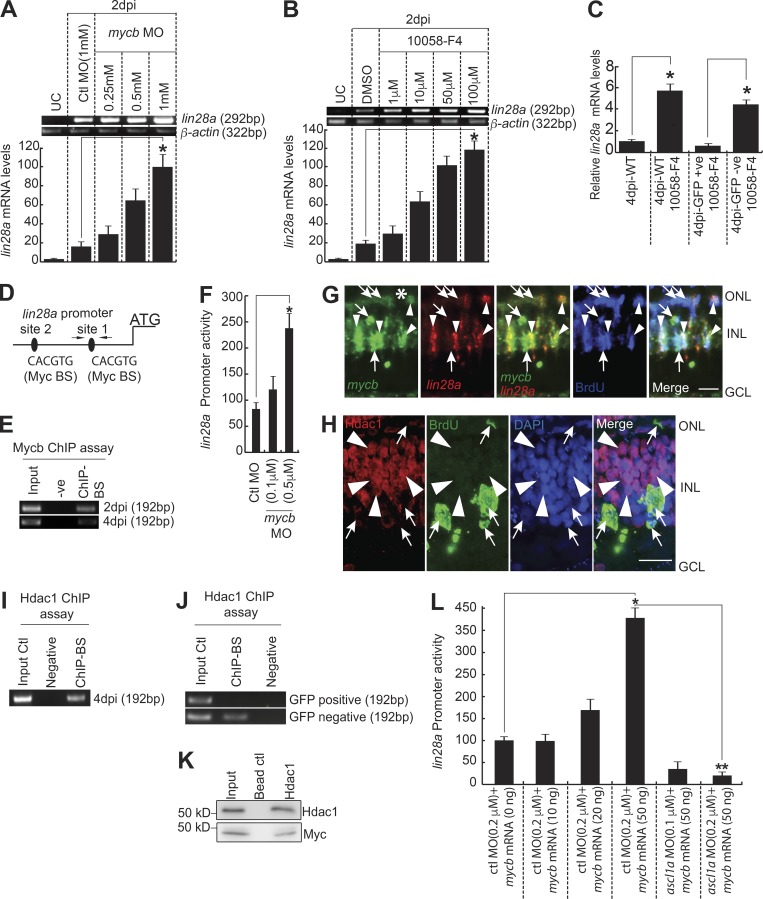
Figure 6.
Mycb-mediated regulation of lin28a in MGPCs. (A and B) RT-PCR (top) and qPCR (bottom) show Myc inhibition using antisense MO (A) or 10058-F4 (B) induce lin28a in 2-dpi retina. *, P < 0.001. UC, uninjured control. (C) qPCR analysis of lin28a mRNA from GFP+ and GFP− cells sorted from 1016 tuba1a:gfp transgenic fish retina with 1-µM 10058-F4 treatment at 4 dpi, compared with WT. *, P < 0.01. (D) Diagram of lin28a promoter with putative Mycb-binding sites. The solid lines represent DNA sequences. Arrows mark ChIP primers, and capital letters mark consensus sequence. (E) The retina ChIP assay at 2 and 4 dpi showed that Myc binds to lin28a promoter. (F) MO-based mycb knockdown up-regulates lin28a:gfp-luciferase activity. Promoter activity is normalized light units with internal control Renilla luciferase. *, P < 0.0002. (G) FISH and IF microscopy show expression of mycb and lin28a with respect to BrdU+ MGPCs in 4-dpi retina. Arrowheads indicate colabel of mycb, lin28a, and BrdU+ cells; arrows indicate mycb+ that colabel with BrdU, but are lin28a− cells. White asterisk marks the injury site. (H) IF and ISH microscopy on a single 0.5-µm thick Z section shows Hdac1 expression secludes largely from BrdU+ cells at the site of injury. Arrowheads mark hdac1+ but BrdU− cells, and arrows mark Hdac1− but BrdU+ cells. (I) ChIP assay using Hdac1 antibody reveals Hdac1 occupied Myc-binding site on lin28a promoter. (J) ChIP assay of lin28a promoter Myc-binding region, using Hdac1 antibody from GFP+ and GFP− cells from 1016 tuba1a:gfp transgenic retina. (K) Co-IP assay using Hdac1 antibody reveals Hdac1–Myc collaboration during retina regeneration. (L) MO-based ascl1a knockdown abrogates Mycb overexpression-mediated lin28a:gfp-luciferase up-regulation in embryos. *, P < 0.0002; **, P < 0.003. n = 6 biological replicates unless specified. Error bars are SD. −ve, negative; +ve, positive; BS, binding site. Bars, 10 µm (G and H). ONL, outer nuclear layer; INL, inner nuclear layer.