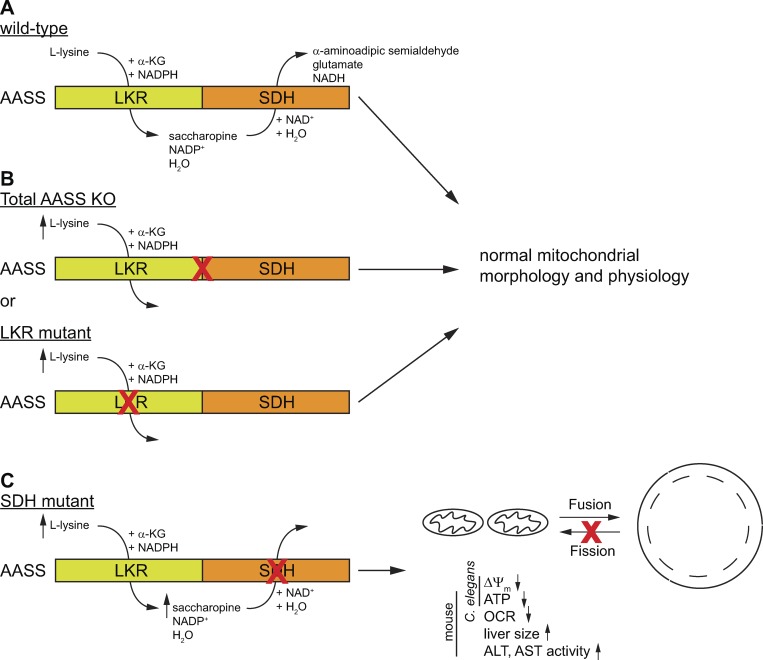
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the consequences of different mutations in AASS on mitochondrial dynamics and function. (A) The wild type AASS consist of two domains. LKR catalyzes the NADPH-dependent formation of saccharopine from lysine and α-KG. SDH catalyzes the NAD-dependent formation of α-aminoapidate semialdehyde from saccharopine. (B) Mutations that produce a total AASS KO or an isolated defect in LKR lead to hyperlysinemia, but without any apparent clinical or mitochondrial consequences. (C) Mutations that cause an isolated defect in SDH lead to hyperlysinemia with saccharopinuria that ultimately produces mitochondrial defects and liver disease in mice. ΔΨm, mitochondrial membrane potential; ALT, plasma alanine aminotransferase; AST, plasma aspartate aminotransferase.