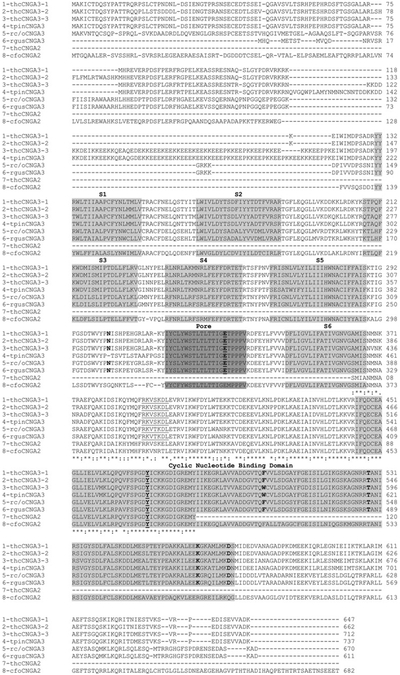
Figure 1. Clustal sequence alignment of the three trout saccular hair cell CNGA3 subtypes.
Line 1, trout hair cell (thc) CNGA3-1 (GenBank® accession number HQ542177). Line 2, trout hair cell CNGA3-2 (GenBank® accession number HQ542178). Line 3, trout hair cell CNGA3-3 (GenBank® accession number HQ542179). Line 4, trout pineal photoreceptor (tpin) CNGA3 (GenBank® accession number AF393839). Line 5, rat cone/olfactory (rc/o) CNGA3 (GenBank® accession number EDL992404 for olfactory protein sequence). Line 6, rat gustatory (rgus) CNGA3 (GenBank® accession number NM_053495). Line 7, trout hair cell CNGA2. Line 8, catfish olfactory (cfo) CNGA2 (GenBank® accession number P55934 for protein sequence). The six transmembrane domains, S1–S6 (light grey), the pore region between S5 and S6 (dark grey) and the CNBD (light grey) are highlighted. The Clustal designations for identity and homology across CNGA3 and CNGA2 sequences are indicated starting at residue 429 and finishing at residue 547 (CNGA3-3). Also in bold and/or underlined are amino acid residues believed to have specific functions in higher vertebrates and which are conserved in the trout hair cell CNGA3 sequence, with numbering according to that of CNGA3-3: N-glycosylation site, Asn367 putatively affecting pore function; predicted PKA site, RKVSKDL in C-linker, amino acids 455–461; Cys513, affecting coupling of cGMP to the pore; Tyr536 within the CNBD, a putative phosphorylation site conserved across CNG subunits in higher vertebrates; Trp566, Thr593, Lys629 and Asp637 within the CNBD represent amino acids thought to be important in specifying cGMP sensitivity in CNGA1 and CNGA3 channels.