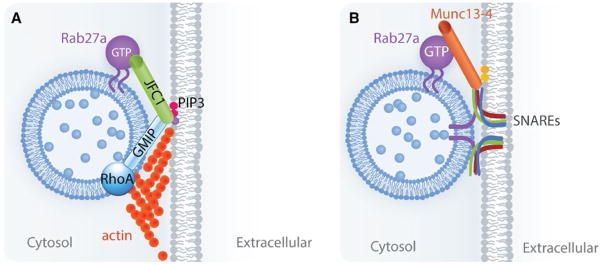
FIGURE 2.
The sequential steps and molecules involved in the exocytosis of azurophilic granules. (A) The Rab27a effector JFC1 associates with the secretory granules by binding to Rab27a through its Rab-binding domain.59 JFC1 interaction with the RhoA-GAP GMIP induces the inhibition of RhoA, facilitating actin depolymerization around the secretory vesicle, thus allowing the vesicles to access the exocytic active zone.80 JFC1 is further capable of causing loose tethering by binding to PIP3 on the plasma membrane through its C2A domain.66 (B) Once the vesicles are in the exocytic active zone, the Rab27a effector Munc13-4 facilitates docking and subsequent SNARE-mediated fusion of the vesicle membrane with the plasma membrane28,69,76