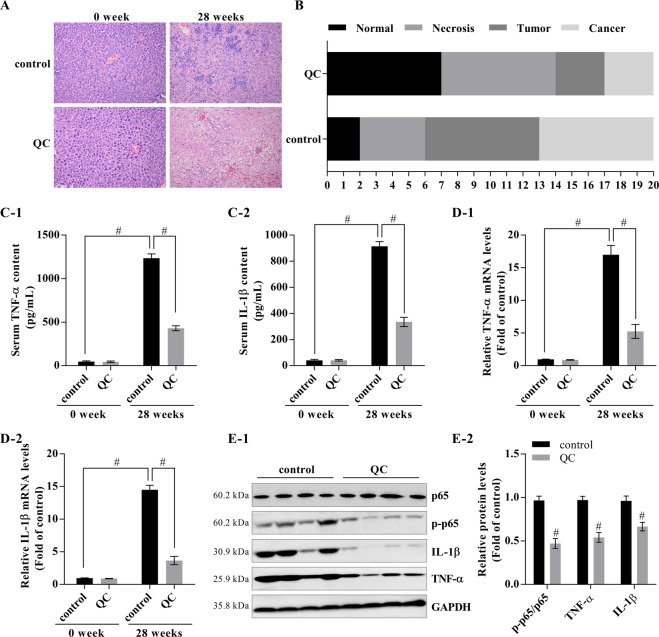
Figure 1.
Inhibitory effect of the Qizhu decoction extracts on DEN-induced hepatitis in mice via NF-κB. Mice were given daily injections of DEN (50 mg/kg i.p.) for 28 weeks; some of the mice were only administered DEN (control), whereas others were also intragastrically administered a Qizhu decoction extract (QC) at 20 g/kg of body weight daily throughout the experimental period. (A) Effect of QC on DEN-induced hepatitis detected by H&E staining. (B) Numbers of mice with DEN-induced hepatitis, necrosis, tumor, and liver cancer. (C) The levels of TNF-α (C-1) and IL-1β (C-2) in mouse serum were analyzed by ELISA. Each value indicates the mean ± SD and is representative of results from three independent experiments; #P < 0.001 vs. the control (0 QC). (D) The mRNA expression of TNF-α (D-1) and IL-1β (D-2) in mouse livers was determined by real-time PCR, and GAPDH was used as an internal control. Each value indicates the mean ± SD and is representative of results from three independent experiments; #P < 0.001 vs. the control (0 QC). (E) The NF-κB activity was analyzed by western blot (E-1), and a corresponding semiquantitative analysis based on optical density was performed using ImageJ software (E-2). The values are presented as the means ± SDs of data from three separate experiments; #P < 0.001 vs. the control (0 QC).