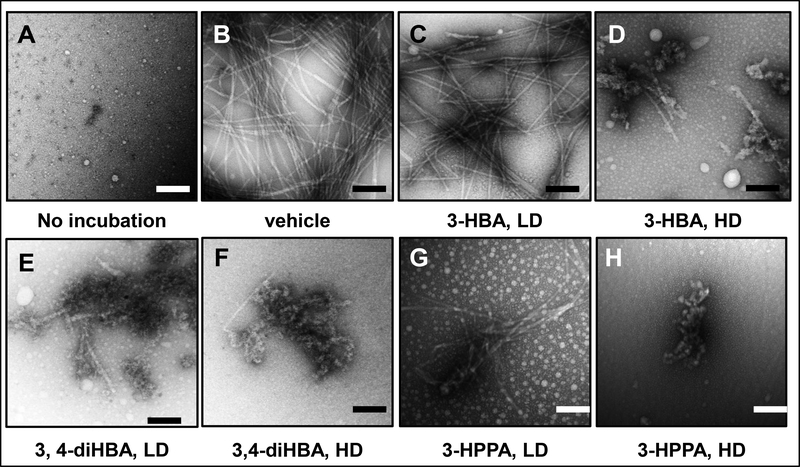
Fig. 5. Effects of brain-accumulating microbial-generated phenolic acid metabolites on α-synuclein protofibril morphology.
Monomeric α-synuclein (70 μM) was incubated in the presence of vehicle or individual brain-accumulating microbial-generated phenolic acid metabolites at 37°C for 94 hours in 20 mM Tris, pH 7.4, 100 mM NaCl. EM was used to determine the morphologies of the resultant α-synuclein assemblies. (A, B) monomeric α-synuclein (A) and α-synuclein incubated in the presence of vehicle (B). (C, D, E, F, G, H) α-synuclein incubated in the presence of individual phenolic acids at a low dose (LD, equal molar concentration of phenolic acid to α-synuclein) or a high dose (HD, 4-fold higher molar concentration of phenolic acid to α-synuclein): LD or HD 3-HBA (C, D), LD or HD 3,4-diHBA (E, F), LD or HD 3-HPPA (G, H). Scale bars indicate 100 nm