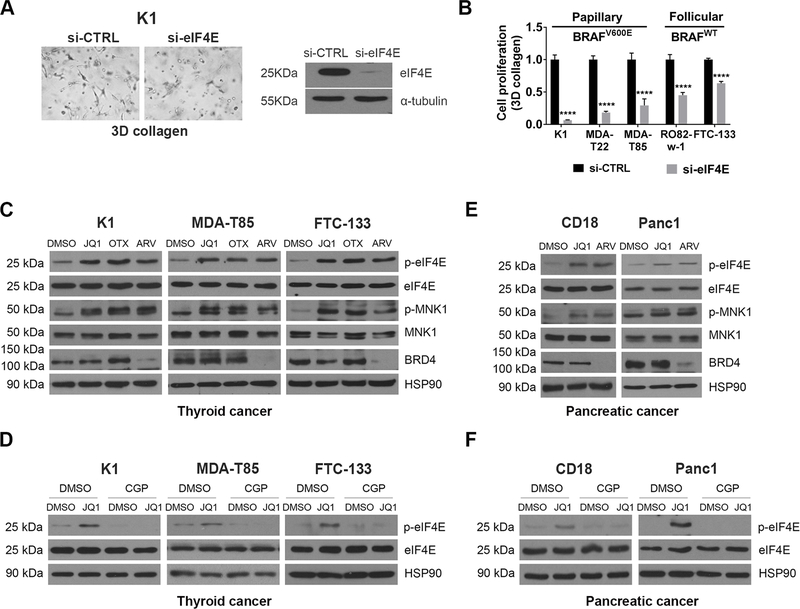
Figure 2: BETis and BET PROTACs induce eIF4E phosphorylation.
A. Thyroid cancer cells were transfected with siRNA targeting eIF4E for 48 hours, and then cultured in 3D collagen for additional 48 hours. The cells were examined by phase microscopy. Knockdown efficiency was determined by Western blotting. B. Thyroid cancer cells with or without BRAFV600E mutation were transfected with siRNA targeting eIF4E for 48 hours and then cultured in 3D collagen for additional 48 hours. The effect on proliferation was determined by WST-1 assay. ****, p<0.0001. C. Thyroid cancer cells were treated with BETis JQ1 (1 μM) and OTX-015 (OTX, 1 μM) or the BET PROTAC ARV-825 (ARV, 1 μM) for 24 hours. The effect on eIF4E and MNK1 phosphorylation and expression of eIF4E, MNK1, BRD4 and HSP90 (loading control) was determined by Western blotting. D. Thyroid cancer cells were pre-treated with CGP57380 (CGP, 10 μM) for 30 min, followed by treatment of JQ1 (1 μM) for 24 hours. The effect on eIF4E phosphorylation and expression of eIF4E and HSP90 was determined by Western blotting. E. CD18 and Panc1 pancreatic cancer cells were treated with the BET inhibitor JQ1 (1 μM) or the BET PROTAC ARV-825 (ARV, 1 μM) for 24 hours. The effect on eIF4E and MNK1 phosphorylation and expression of eIF4E, MNK1, BRD4 and HSP90 (loading control) was determined by Western blotting. F. Pancreatic cancer cells were pre-treated with CGP57380 (CGP, 10 μM) for 30 min and then treated with JQ1 (1 μM) and for 24 hours. The effect on eIF4E phosphorylation and expression of eIF4E and HSP90 was determined by Western blotting. The results are representative of at least three independent experiments.