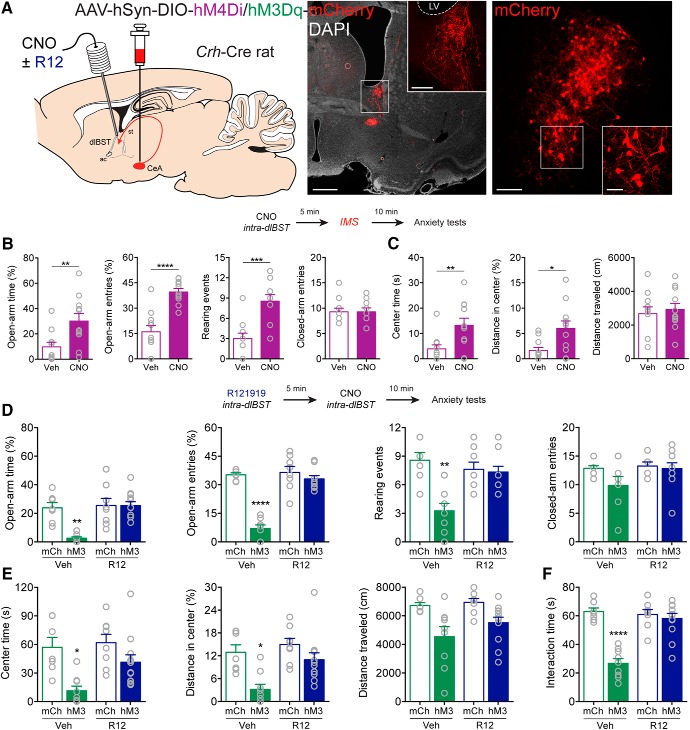
Figure 4.
CRFCeA projections to dlBST mediate anxiety. A, AAV encoding Cre-dependent inhibitory hM4Di or excitatory hM3Dq was injected into the CeA with guide cannulas directed to the dlBST for targeted CNO microinjection. Left, CRFCeA fibers targeting the dlBST. Scale bar, 500 μm. Boxed region is enlarged in inset. Scale bar, 50 μm. Right, dlBST-projecting CRFCeA neurons. Scale bar, 200 μm. Boxed region is enlarged in inset. Scale bar, 20 μm. B, Inhibition of CRFCeA terminals in the dlBST with CNO (1 mm in 0.3 μl) increased the percentage of time spent on the open arms of the EPM, the percentage of open arm entries, and the number of rearing events without affecting the number of closed arm entries. C, Activation of hM4Di with CNO also increased time spent in the center of the OF and the distance traveled in the center without altering the total distance traveled after IMS. D, Activation of CRFCeA terminals in the dlBST with CNO (1 mm in 0.3 μl) reduced the percentage of time spent on the open arms of the EPM, the percentage of open arm entries, and the number of rearing events, which was prevented with local injection of R121919 (1 μg in 0.3 μl). E, Activation of terminals also reduced time spent in the center and distance traveled in the center of the OF, which was prevented by local blockade of CRF1 receptors. CNO modestly reduced the total distance traveled in the OF in animals that expressed hM3Dq in CRFCeA neurons, whereas R121919 in the dlBST had no effect. F, Terminal activation reduced social interaction time, which was CRF1 receptor-dependent. Data are mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. Veh (vehicle), R12 (R121919), mCh (mCherry), hM3 (hM3Dq), LV (lateral ventricle).