Figure 9.
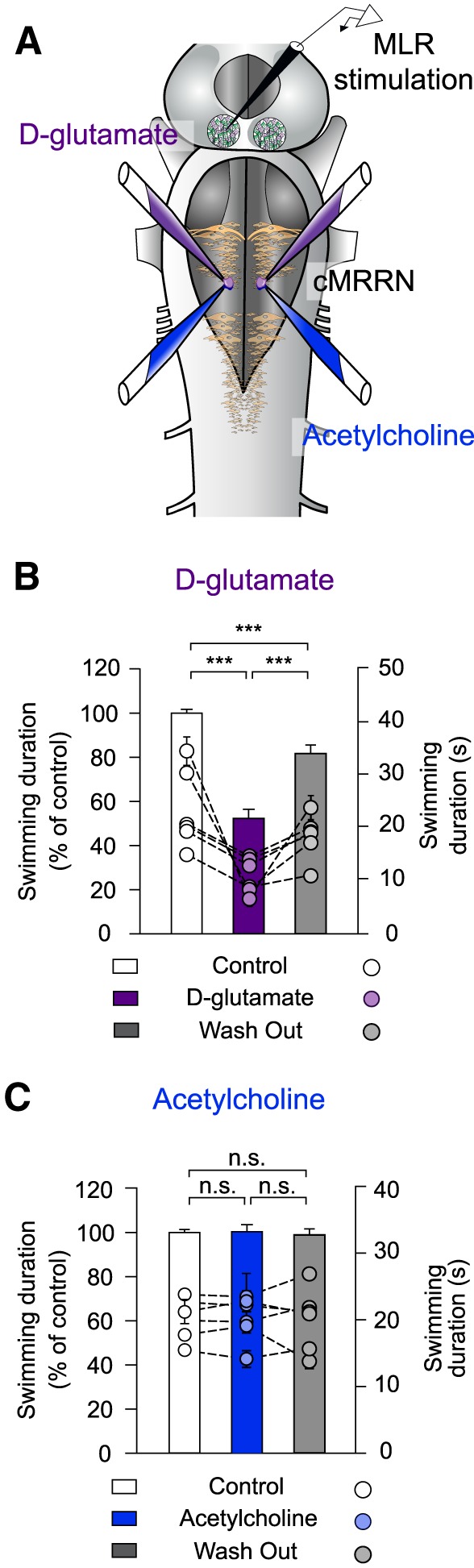
Effects of injecting glutamatergic and cholinergic agonists into the stop cell region. A, In a semi-intact preparation, bilateral injections of d-glutamate or acetylcholine were made in the stop cell region (caudal MRRN) and electrical MLR stimulation was used to induce locomotion. Injection and stimulation sites are illustrated in the schematic representation of the brainstem. B, d-Glutamate was bilaterally injected into the stop cell region during MLR-induced swimming. Compared with control conditions (white bar), swimming duration was significantly shortened by a local d-glutamate injection (violet bar) and this effect was reduced after a washout period of 1 h (gray bar). C, Acetylcholine was bilaterally injected into the stop cell region during MLR-induced swimming. The duration of swimming was not significantly altered compared with control conditions (white bar), when acetylcholine was locally injected in the caudal MRRN (blue bar), or after a washout period of 1 h (gray bar). Data were normalized to the mean of control. In both experiments, bars represent the mean ± SEM of pooled data (n = 30 trials in 6 animals for each condition; left y-axis). Dots illustrate mean ± SEM of raw data for each animal (right y-axis). ***p < 0.001; n.s. not statistically significant.
