FIG 1.
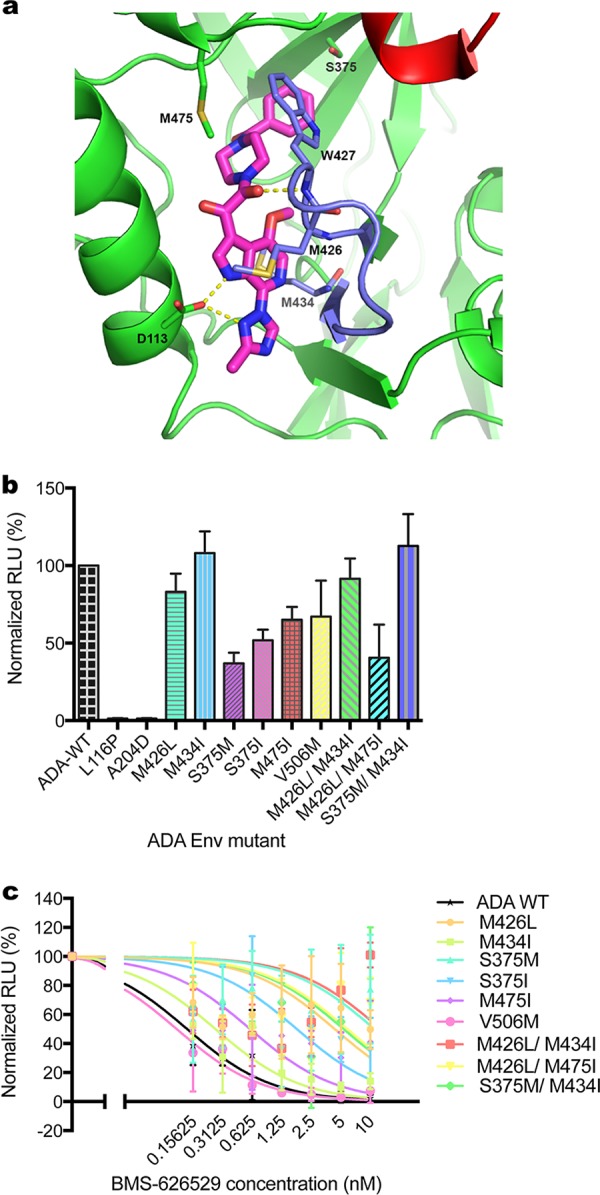
Reduced susceptibility of escape mutants to BMS-626529. (a) Crystal structure of HIV-1 BG505 SOSIP.664 prefusion Env trimer bound to BMS-626529, in complex with bNAb PGT-122 and 35O22 at 3.8-Angstrom resolution (PDB code: 5U7O) (5). BMS-626529 predominantly binds to gp120 via hydrophobic interactions and forms hydrogen bonds with D113 from the α1-helix of the gp120 inner domain and W427 of the outer domain. The benzamide group of BMS-626529 occupies the site of gp120 that is occupied by W427 in the open state such that W427 and the β20-β21 loop are extended toward the CD4 binding loop (red), thereby blocking CD4 binding. Major escape mutation sites of BMS-626529 including M426, S375, M434 and M475, are shown. (b) Pseudotype titer of reconstructed BMS-626529-resistant mutations introduced in ADA Env. GHOST.Hi5 cells were transduced with identical volumes of supernatant of HIV-LIB pseudotyped with each mutant Env. RLU levels in transduced cells were measured and normalized to those of wild-type Env. The data represent means ± standard deviations (SD) of results from three experiments. (c) Neutralization of wild-type and mutant ADA Env pseudotyped virus by BMS-626529. The means ± SD of results from three independent experiments are shown.
