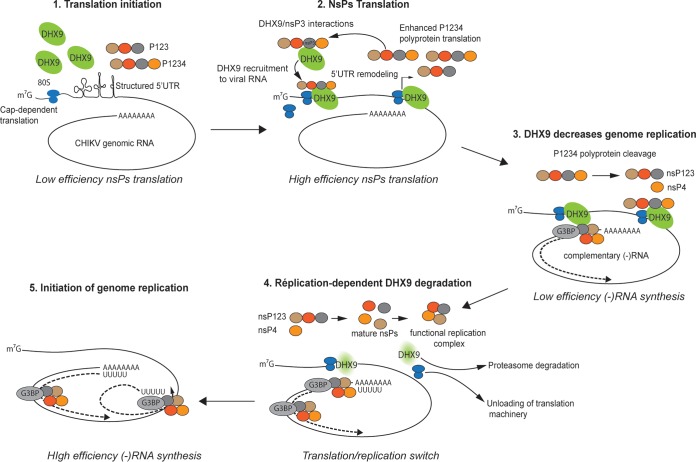
FIG 10.
Model of DHX9-dependent regulation of the alphavirus translation-to-replication switch. DHX9 is recruited to the plasma membrane-bound replication complexes through interactions with the HVD domain in nsP3, where it enhances nsP translation. As translation and nsP precursor cleavage proceeds, the concentration of mature nsP2 increases, accounting for DHX9 unloading from the replication complex and redirection to proteasomal degradation. In the absence of DHX9, translation is shut down, and replication starting with (–)RNA synthesis is favored. G3BP recruitment to replication complexes is depicted in this model.