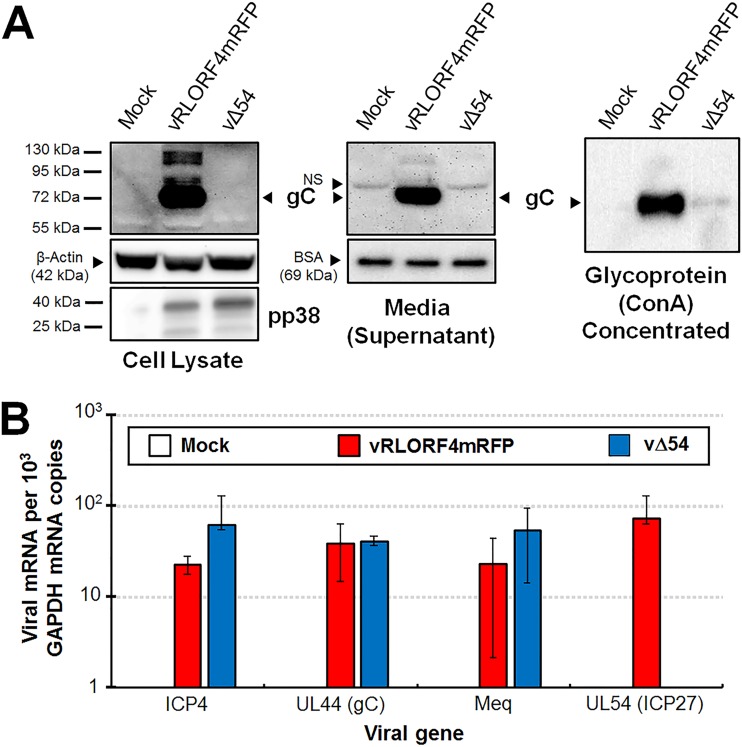
FIG 5.
MDV ICP27 is required for gC protein expression in cell culture. CKCs in 60-mm dishes were infected with 500 PFU of each respective virus. (A) Total cellular protein and cell culture media (supernatant) were collected from mock-, vRLORF4mRFP-, or vΔ54-infected cells at 5 dpi and used in Western blots. Anti-β-actin and -BSA were used for loading controls of cellular and supernatant samples, respectively. Anti-pp38 mAb was used to show comparable infection levels of infected cell cultures. ConA pulldown was used to concentrate glycoproteins. No endogenous control is available for ConA pulldown, but equal amounts of supernatant were used in the pulldown assay. No cellular or secreted MDV gC could be detected in vΔ54-infected CKCs, while abundant gC was present in vRLORF4mRFP-infected cells and supernatant. (B) Total RNA was collected from infected CKCs, cDNA was prepared, and RT-qPCR assays were performed. Specific primers for MDV ICP4, UL44 (gC), Meq (control for gene not expected to be regulated by ICP27), and UL54 (ICP27) were used to quantitate mRNA compared to GAPDH using standard curves. SDs are shown. No amplification of UL54 was detected in vΔ54-infected cells. No significant differences were observed using Student’s t test assuming equal variances at a significance level of P < 0.05. Thus, the lack of gC protein expression in vΔ54 is not due to a lack of mRNA transcription of gC but occurs at the posttranscriptional level.