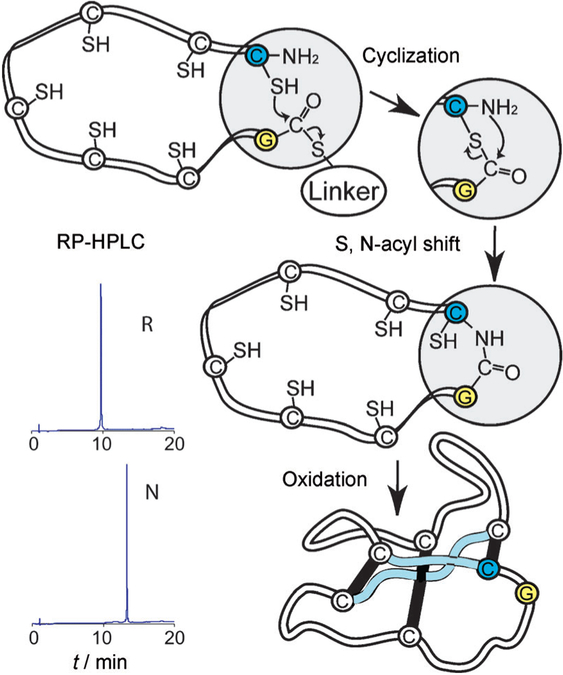
Figure 2.
Scheme for the cyclization and folding of synthetic kalata B1. After the assembly of D amino acids by using manual SPPS with Boc chemistry (see the sequence in Figure 1), D-kalata B1 was cyclized and folded. In a proposed mechanism,[23] the C-terminal thioester, attached through a linker, reacts successively with the cysteine side chains, which act as intermediate nucleophiles and “zip” the activated C terminus towards the N-terminal cysteine, where a final S,N-acyl migration creates a native peptide bond. For clarity, only the last nucleophilic attack is shown. RP-HPLC traces show the increase in hydrophobicity from linear reduced (R) to natively folded (N) protein.