Figure 1. Origin and composition of rabbit mAbs for diagnostic and therapeutic applications.
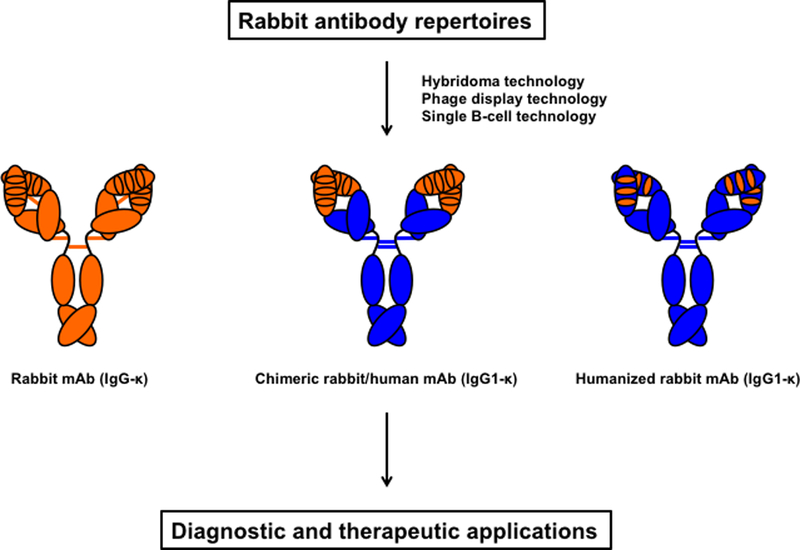
Rabbit antibody repertoires are mined by hybridoma, phage display, and single B-cell technologies to yield rabbit mAbs (here shown in the most common IgG-κ format with 5 interdomain disulfide bridges) or chimeric rabbit/human mAbs (here shown in the most common IgG1-κ format with 4 interdomain disulfide bridges). Rabbit variable (depicted with its 3 CDRs) and constant domains are shown in orange, human domains in blue. While rabbit antibody repertoires from immunized rabbits are the most common source of rabbit mAbs, a large naïve rabbit antibody repertoire that circumvents immunization has recently been generated for mining rabbit mAbs by phage display technology (Peng et al 2017). Chimeric rabbit/human mAbs combine rabbit variable domains of light and heavy chain with human constant domains. Humanized rabbit mAbs, which are preferred for therapeutic applications, are generated by grafting the 6 CDRs into human framework regions. For detailed information on rabbit heavy and light chain isotypes as well as rabbit mAb generation and humanization, please see Weber et al 2017.
