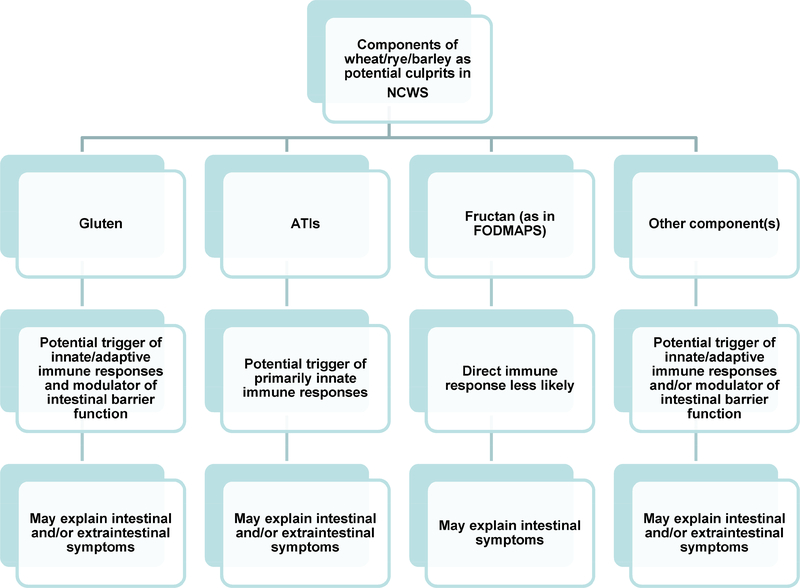
Figure 3:
Different components of wheat, such as gluten, fructans (as part of fermentable oligo-, di-, and mono-saccharides, and polyols, FODMAPs), amylase-trypsin inhibitors (ATIs), and other molecules may act as triggers of non-celiac wheat sensitivity (NCWS), including immune system modulation, intestinal barrier disruption, and symptom generation.