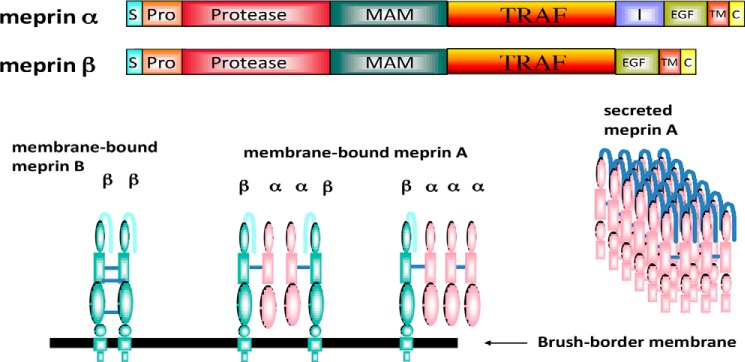
Figure 2.
Domain and oligomeric structure of meprins α and β. Domains are as follows: S (signal sequence), Pro (prosequence), protease, catalytic domain, MAM (meprin), A5 protein, protein-tyrosine phosphatase μ, TRAF homology, I (inserted), EGF (epidermal growth factor-like), TM (transmembrane-spanning), and C (cytoplasmic). During maturation, the meprin α subunit is cleaved in the I domain, separating the subunit from the membrane. As a result, three isoforms of meprin exist: membrane-bound meprin B (a homodimer of β subunits), membrane-bound meprin A (heterotetramers of α and β subunits, found in ratios of α2β2 and α1β3), and secreted meprin A (homomeric multimers of α subunit dimers). The secreted forms of meprin α dimers tend to self-associate and form large multimers (1–6 MDa) extracellularly.