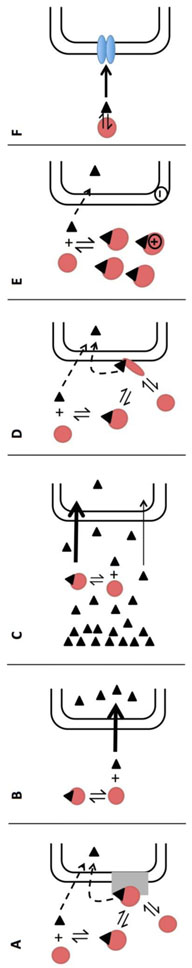
Fig. 5: Hypotheses to explain albumin-facilitated uptake.
A) Presence of an albumin receptor where uptake can occur due to direct uptake of unbound ligand or after specific interaction of the albumin-ligand complex with its receptor; B) Rate-limiting dissociation where free ligand uptake is faster than ligand dissociation from albumin; C) Rate-limiting diffusion of ligand through the UWL where the slow diffusion of unbound ligand is supplemented with the diffusion of more soluble bound ligand; D) Conformational change where uptake occurs from the direct uptake of unbound ligand in plasma or after a conformational change of the albumin-ligand complex due to cell membrane binding catalyzing the release of drug; E) Ionic interactions with the cell membrane where the diffusional distance for unbound ligand is decreased; and F) Transporter-induced protein binding shift where a high affinity transporter may strip ligand from the ligand-drug complex.