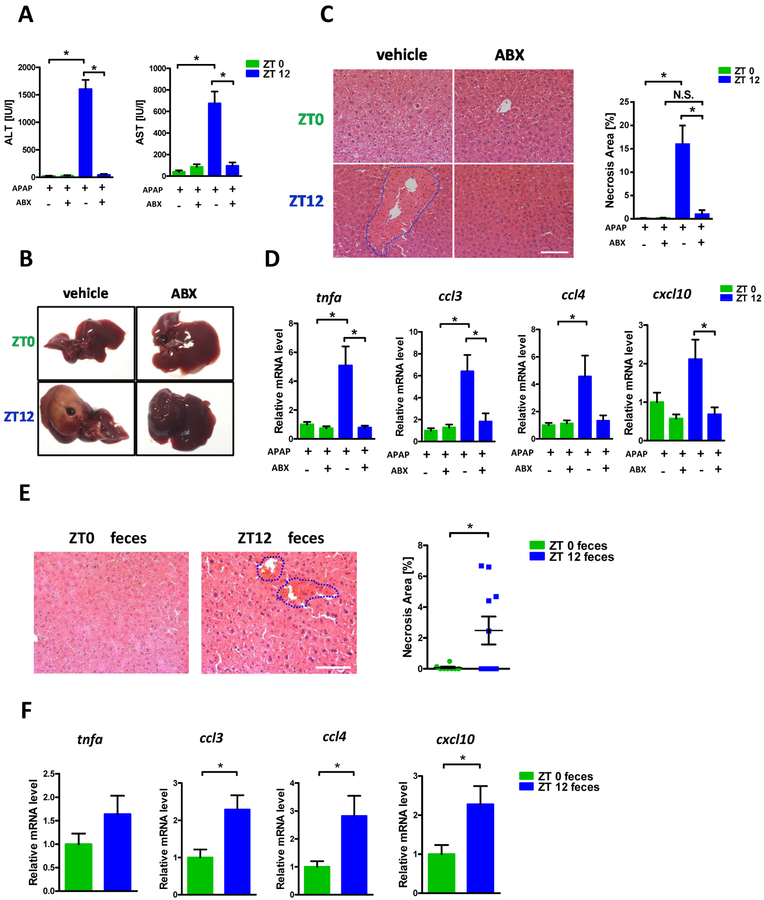
Figure 1:
The diurnal variation of APAP induced hepatotoxicity was dependent on gut microbiota. Balb/C mice were treated with APAP for 24 hours with or without antibiotics pretreatment. (A) Plasma ALT, AST levels (n=6–12). (B) Representative gross liver appearance. (C) Hepatic HE staining and quantification of necrotic area (n=6–12). (D) mRNA levels of key cytokines and chemokines in the liver (n=6–12). (E) Mice received antibiotics intragastrically once daily for 5 days followed by receiving the cecal content from the donor mice (ZT0 or ZT12 group) once daily for 3 days. Mice were then gavaged with 300mg/kg APAP at ZT0 and were sacrificed 24 hours after APAP treatment. HE staining (n=6–12). (F) mRNA levels of key cytokines and chemokines in the liver (n=6–12). ZT0 = 8am. ZT12 = 8pm. The results are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M. Two-tailed Student’s t-test was used for statistical evaluation. *p<0.05. Scale bar: 100 μm. N.S.: non-siginificance.