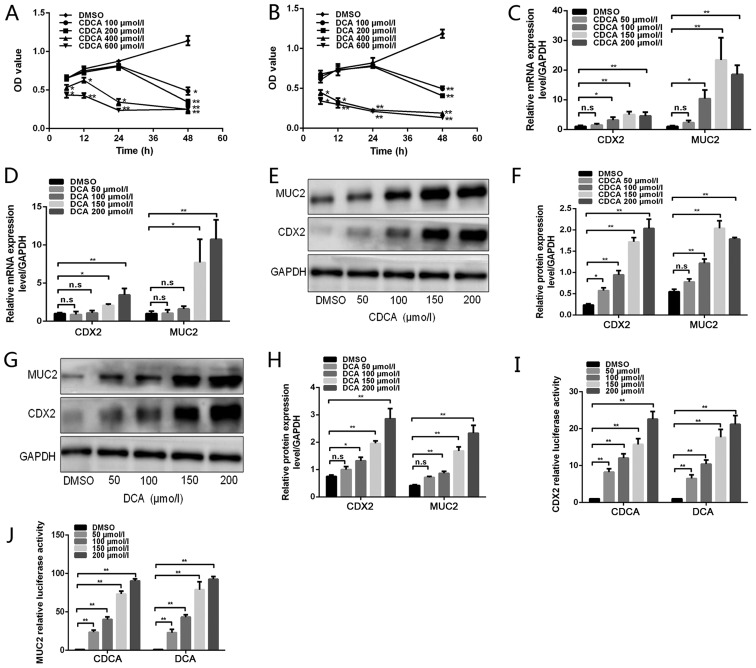
Figure 1.
Effects of bile acids on CDX2 and MUC2 expression in GES-1 cells. (A and B) GES-1 cells were treated with DMSO or various doses of bile acids (100, 200, 400 and 600 µmol/l) for different periods of time (6, 12, 24 and 48 h). Cell viability was then determined using a Cell Counting Kit 8 assay. (C and D) GES-1 cells were treated with DMSO or various concentrations of bile acids (50, 100, 150 and 200 µmol/l) for 24 h. Reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction was performed to determine the mRNA expression levels of CDX2 and MUC2 in GES-1 cells treated with bile acids. (E) Western blot analysis of CDX2 and MUC2 protein expression in each group of GES-1 cells stimulated with CDCA. (F) Comparison of CDX2 and MUC2 protein levels in each group of cells stimulated with CDCA. (G) Western blot analysis of CDX2 and MUC2 protein expression in each group of GES-1 cells stimulated with DCA. (H) Comparison of CDX2 and MUC2 protein levels in each group of cells stimulated with DCA. (I and J) GES-1 cells treated with various concentrations of bile acids were transfected with 2.5 kb CDX2- or 2.6 kb MUC2-luc promoter constructs. A dual-luciferase reporter assay was conducted to determine (I) CDX2 and (J) MUC2 promoter activity. Data are presented as the means ± standard deviation from three independent experiments. *P<0.05, **P<0.01. CDCA, chenodeoxycholic acid; CDX2, caudal-related homeobox transcription factor 2; DCA, deoxycholic acid; DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; MUC2, mucin 2; n.s., not significant; OD, optical density.