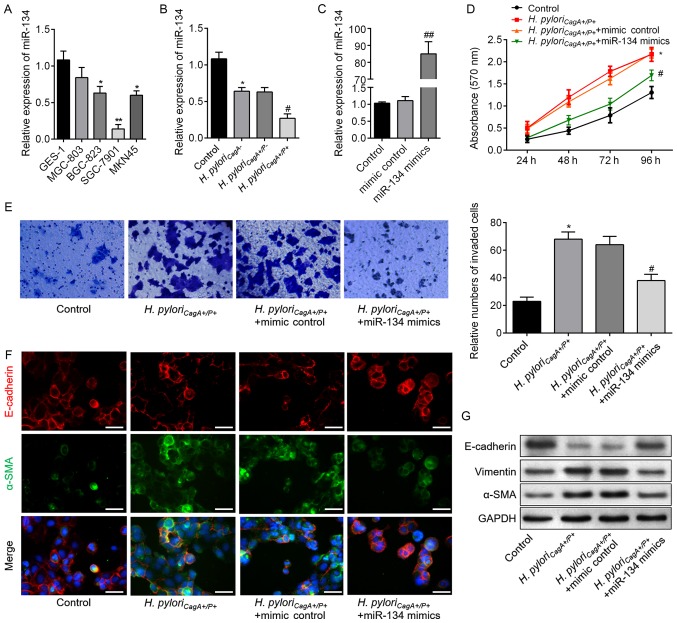
Figure 3.
miR-134 inhibits proliferation, invasion and EMT in H. pyloriCagA+/P+-infected SGC-7901 cells. (A) miR-134 expression in a human gastric epithelial cell (GES-1), and MGC803, BGC-823, SGC-7901 and MKN45 gastric cancer cell lines, as detected by reverse transcription-qPCR analysis. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs. GES-1 cells. (B) Relative expression levels of miR-134 in SGC-7901 cells infected with H. pyloriCagA-, H. pyloriCagA+/P- and H. pyloriCagA+/P+. (C) Expression levels of miR-134 in SGC-7901 cells transfected with mimic control or miR-134 mimics, as evaluated by reverse transcription-qPCR assay. (D) SGC-7901 cells transfected with miR-134 mimics or mimic control under H. pyloriCagA+/P+ infection were subjected to Cell Counting Kit-8 analysis. (E) Invasive SGC-7901 cells were stained with 0.1% crystal violet and counted 48 h post-transfection (magnification, ×100). The number of invaded cells was determined from three replicate wells and data are expressed as the means ± standard deviation. (F) Double-labeled immunofluorescence staining was performed to examine the expression of E-cadherin (red) and α-SMA (green) in SGC-7901 cells from the various groups. Images merged with DAPI are presented. Scale bar, 50 µm. (G) Protein expression levels of E-cadherin, Vimentin and α-SMA in SGC-7901 cells treated as indicated. *P<0.05 vs. the control group; #P<0.05 vs. the H. pyloriCagA+/P+ + mimics control group. α-SMA, α-smooth muscle actin; CagA, cytotoxin-associated gene A; H. pyloriCagA-, CagA-negative H. pylori; H. pyloriCagA+/P−, CagA-positive and PBP1A mutation-negative H. pylori; H. pyloriCagA+/P+, CagA- and PBP1A mutation-positive H. pylori; H. pylori, Helicobacter pylori; miR-134, microRNA-134; PBP1A, penicillin-binding protein 1A; RT-qPCR, reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction.