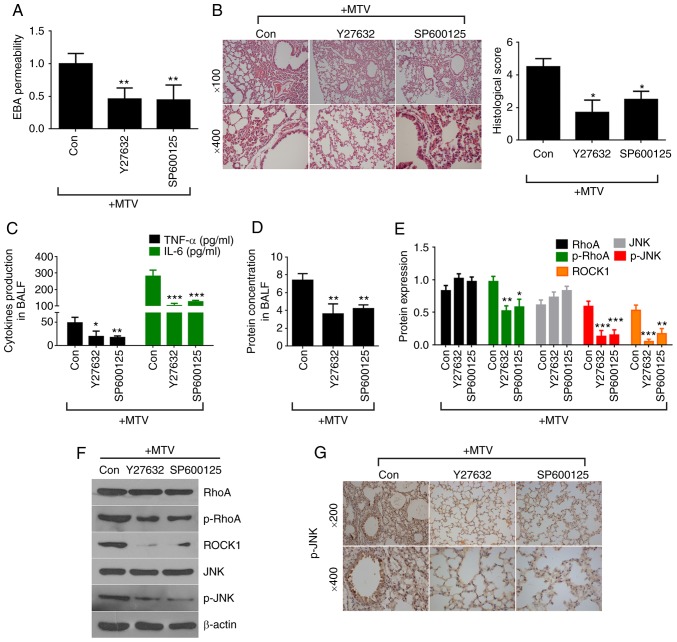
Figure 7.
Inhibition of non-canonical Wnt signaling attenuates MTV-induced lung injury. (A) EBA permeability was decreased in A/J mice administered Y27632 or SP600125 prior to MTV ventilation compared to mice ventilated with MTV alone (n=3). (B) Administration of Y27632 or SP600125 reduced MTV-induced inflammatory cell infiltration, pulmonary edema, alveolar septal thickening and histological scores (n=4-6). (C) TNF-α and IL-6 expression, as well as (D) total protein concentration decreased in BALF in A/J mice following the administration of Y27632 or SP600125 prior to MTV ventilation (n=4-6). (E) Protein quantification in Y27632 or SP600125 treatment reduced the ventilation-induced increase in p-RhoA, p-JNK and ROCK1. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs. control. (F) Western blotting for p-RhoA, p-JNK and ROCK1 protein expression in A/J mice after administering Y27632 or SP600125 prior to MTV ventilation. (G) Immunohistochemical staining for p-JNK expression was decreased in A/J mice following the administration of Y27632 or SP600125 prior to MTV ventilation. BALF, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid; EBA, Evan's blue albumin; MTV, moderate tidal volume; p-, phosphorylated; JNK, c-Jun N terminal kinase; ROCK1, Rho-associated protein kinase 1; RhoA, Ras homolog gene family, member A; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; IL-6, interleukin 6; Y27632, ROCK1 inhibitor; SP600125, JNK inhibitor.