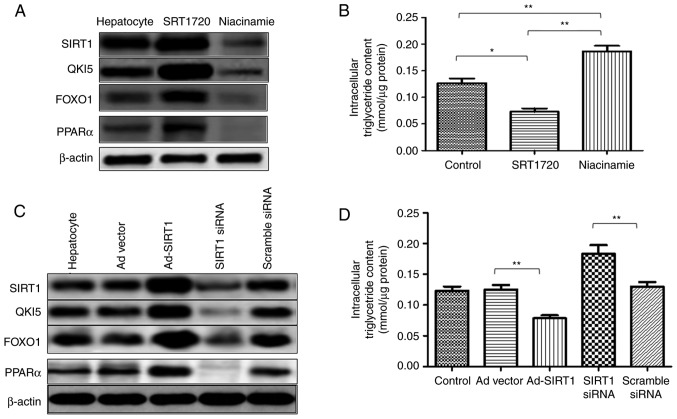
Figure 6.
Hepatic SIRT1 regulates the synthesis of triglycerides in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease mice via the PPARα/FoxO1 signaling pathway in vivo. In primary hepatocytes, SRT1720 enhanced the expression of SIRT1, QKI 5, FOXO1 and PPARα. (A) Expression of SIRT1 was reduced by niacinamide, which also induced the downregulation of QKI 5, FOXO1 and PPARα. (B) Decreased intracellular triglyceride content was caused by SRT1720, whereas niacinamide enhanced the triglyceride content in primary hepatocytes. (C) In primary hepatocytes, Ad-SIRT1 enhanced the expression of SIRT1, QKI 5, FOXO1 and PPARα, which was inhibited by siRNA of SIRT1. (D) SRT1720 reduced the triglyceride content in primary hepatocytes, which was promoted by SIRT1 siRNA. The data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation from three independent experiments. *P<0.05 and **P<0.01. PPARα, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α; FOXO1, Forkhead box protein O1; QKI 5, Quaking 5; SIRT1, Sirtuin 1; siRNA, small interfering RNA; Ad, adenovirus.