Fig. 4. Neutrophils polarized by superlow-dose LPS aggravate atherosclerosis.
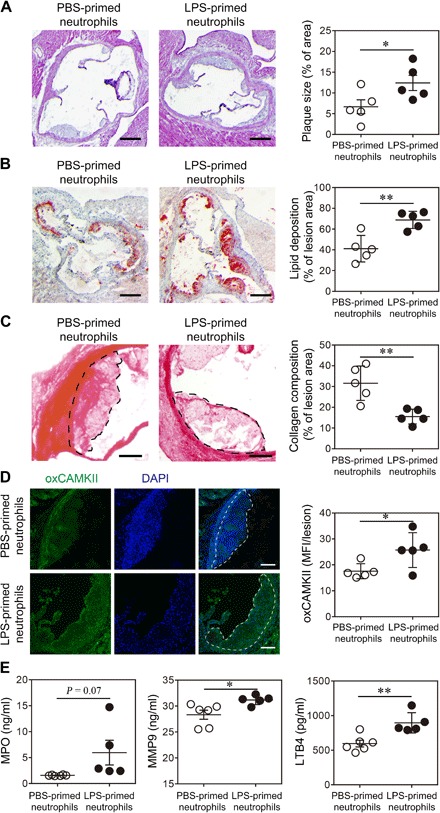
Neutrophils purified from ApoE−/− mice were treated with PBS or superlow-dose LPS (100 pg/ml) for 24 hours. PBS- or LPS-polarized neutrophils (2 × 106 cells per mouse) were then adoptively transferred by intravenous injection to HFD-fed ApoE−/− mice once a week for 4 weeks. Samples were collected 1 week after the last neutrophil transfer. (A) Representative images of H&E-stained atherosclerotic lesions and quantification of plaque size exhibited as the percentage of lesion area within aortic root area. Scale bars, 300 μm. (B) Representative images of Oil Red O–stained atherosclerotic plaques and quantification of lipid deposition within lesion area. Scale bars, 300 μm. (C) Representative images of Picrosirius red–stained atherosclerotic plaques and quantification of collagen content within lesion area. Scale bars, 100 μm. (D) Representative images and quantification of lesional oxCaMKII levels by confocal microscopy. Scale bars, 100 μm. DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole. (E) Determination of circulating MPO, MMP9, and LTB4 levels by ELISA. Data are representative of two independent experiments, and error bars represent means ± SEM. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01, Student’s t test (n = 5 to 6 for each group).
