Fig. 1. c-Abl kinase reduces HBV replication and HBV polymerase protein level.
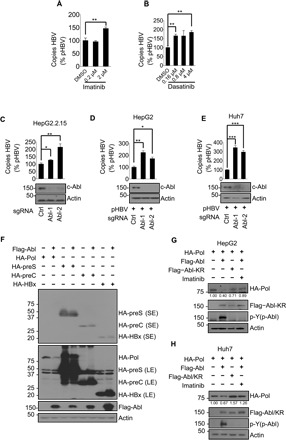
(A and B) Quantitation of capsid-associated viral DNA by real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR). HepG2.2.15 cells were treated with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) or imatinib (A) or dasatinib (B) in indicated concentrations for 24 hours before harvest. Mean copy number from cells treated with DMSO was set to 100% and compared with others. Statistical significance compared with DMSO is noted by asterisks (n = 3 to 4 per group). (C) Quantitation of capsid-associated viral DNA by real-time PCR in HepG2.2.15 cells knocking out control (sgCtrl) or Abl (sgAbl-1/2). Mean copy number from sgCtrl cells was set to 100% and compared with others (n = 3 per group). (D and E) Quantitation of capsid-associated viral DNA by real-time PCR in HepG2 cells (D) or Huh7 cells (E) knocking out control or Abl. Cells were transfected with pHBV for 48 hours before harvest. Mean copy number from sgCtrl cells was set to 100% and compared with others (n = 3 per group). (F) Human embryonic kidney (HEK) 293T cells were cotransfected with constructs expressing hemagglutinin (HA)–tagged polymerase (HA-Pol), preS (HA-preS), preC (HA-preC), and HBx (HA-HBx), and Flag-tagged Abl (Flag-Abl) or empty vector controls. SE, short exposure; LE, long exposure. Western blot was performed 48 hours after transfection. HepG2 cells (G) or Huh7 cells (H) were transfected as shown. Cells were treated with DMSO or 2 μM imatinib for 24 hours before harvest. Total cell lysates were then analyzed for the indicated proteins. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001.
