Figure 4. Hypothetical etiology model for explaining SD pathogenesis mechanisms.
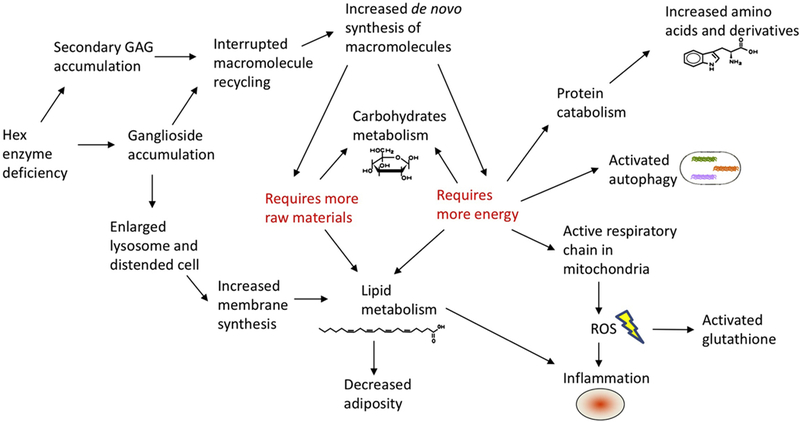
Based on metabolomics profiling, bioinformatics analysis and previous literature, a hypothetical etiology model was proposed. Hex enzyme deficiency causes ganglioside and GAG accumulation, which may lead to interrupted macromolecule recycling and increased de novo synthesis of macromolecules. On the other hand, ganglioside accumulation could result in enlarged lysosome and distended cell, which in turn affects lipid metabolism. Both pathways require more raw materials and more energy. A series of events including protein catabolism, activated autophagy, active respiratory chain in mitochondria may follow.
