Figure 1.
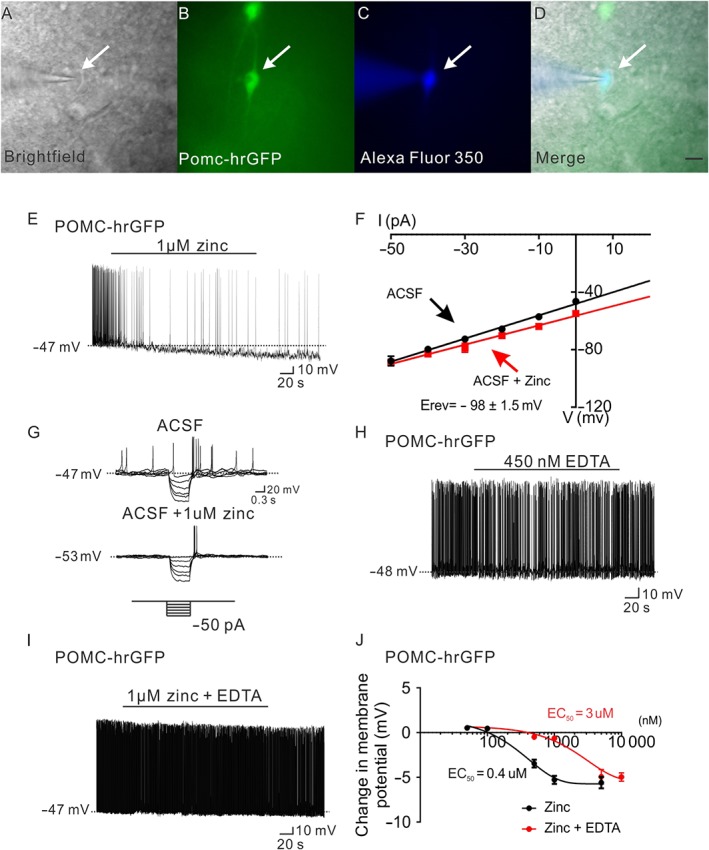
Zinc hyperpolarizes POMC neurons in the arcuate nucleus of hypothalamus. (A–D) Brightfield illumination (A) of POMC neuron from POMC‐hrGFP mice. (B) Shows the same neuron under FITC (hrGFP) illumination. Complete dialysis of Alexa Fluor 350 from the intracellular pipette is shown in (C) and merged image of targeted POMC neuron (D). Arrow indicates the targeted cell. Scale bar = 50 μm. (E) Current‐clamp recording demonstrates that administration of zinc (1 μM) hyperpolarized POMC neurons. (F) Current versus voltage (I–V) relationship for the group of POMC neurons examined in response to zinc (1 μM). (G) Current‐clamp recording from a POMC neuron showing a decreased voltage deflection in response to current injection after zinc application. (H,I) Application of EDTA has no effect on the membrane potential of POMC neurons, and administration of EDTA blunted zinc (1 μM) induced hyperpolarization of POMC neurons. (J) Dose‐response to zinc and zinc + EDTA on POMC neurons. (zinc: n = 39; zinc + EDTA: n = 50. Data from 21 mice.)
