Figure 4.
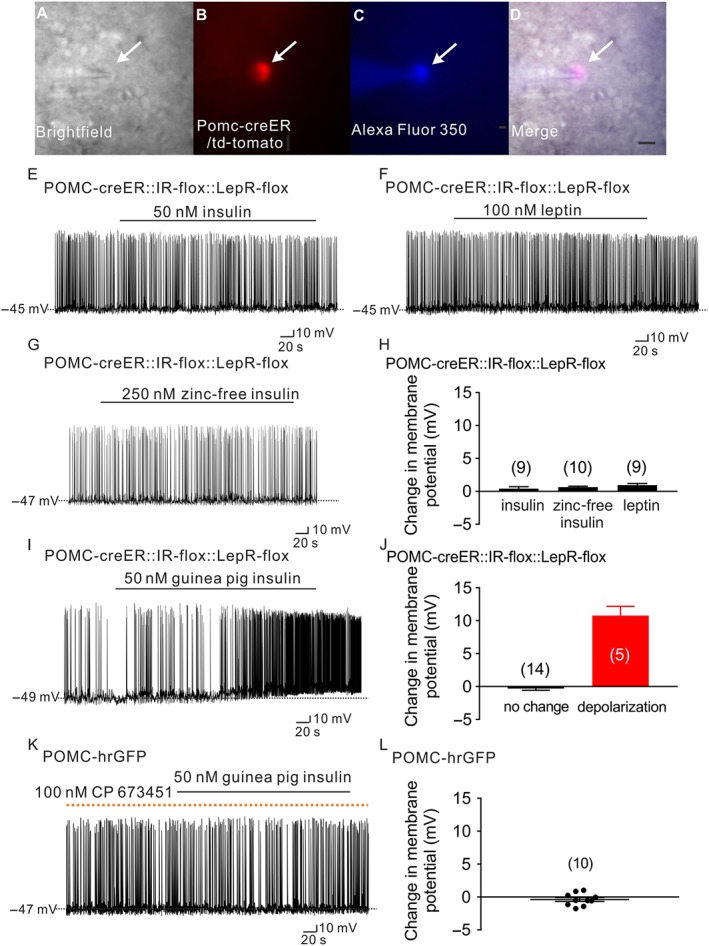
Guinea pig insulin activates arcuate POMC neurons dependent on PDGF receptors, independent of leptin receptors or insulin receptors. (A–D) Brightfield illumination (A) of POMC neuron from POMC‐creER::IR‐flox::LepR‐flox::td‐tomato mice. (B) Shows the same neuron under TRITC (td‐tomato) illumination. Complete dialysis of Alexa Fluor 350 from the intracellular pipette is shown in (C) and merged image of targeted POMC neuron (D). Arrow indicates the targeted cell. Scale bar = 50 μm. (E–G) Current‐clamp record demonstrates that insulin (50 nM, Humulin‐R), leptin (100 nM) and zinc‐free insulin (250 nM) fail to alter the cellular excitability of POMC neurons deficient for leptin receptors and insulin receptors from POMC‐creER::IR‐flox::LepR‐flox::td‐tomato mice. (H) Histogram illustrates insulin‐ and leptin‐induced changes of membrane potential of POMC neurons from POMC‐creER::IR‐flox::LepR‐flox::td‐tomato mice. Data shown are means ± SEM from 10 mice; insulin: n = 9; zinc‐free insulin: n = 10; leptin: n = 9, they have added 10 mice). (I) A representative trace shows that POMC neurons which are deficient for leptin receptors and insulin receptors are depolarized by guinea pig insulin (50 nM). (J) Histogram illustrates guinea pig insulin‐induced change of membrane potential of POMC neurons from POMC‐creER::IR‐flox::LepR‐flox::td‐tomato mice. Error bars indicate SEM; n = 19; data from six mice. (K) A representative trace demonstrates that pretreatment with the PDGF receptor antagonist, CP 673451, prevents the guinea pig insulin (50 nM) induced depolarization of POMC neurons. Dotted line: treatment of CP 673451. (L) Histogram illustrates guinea pig insulin‐induced change of membrane potential of POMC neurons after pretreatment with CP 673451. Values shown are means with SEM; n = 10; data from four mice.)
