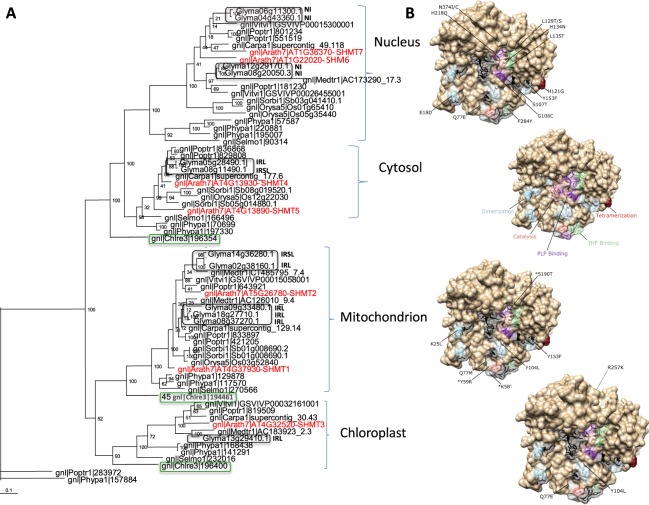
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic tree of SHMT classes from sequenced plant species. (A) All SHMT proteins identified in five model plants; C. reinhardtii (algae; green box), P. patens (moss), S. moellendorfii (lycophyte), O. sativa (monocot), and A. thaliana (eudicot), in addition to G. max (soybean; black box) and other monocots and eudicots cytosolic, nucleic, chloroplastic, and mitochondrial-localized SHMTs were included in the analysis. SHMTs (in red) from A. thaliana belong to mitochondrial SHMT1 (AT4g37930) and SHMT2 (AT5g26781), the chloroplastic SHMT3 (AT4g32520), the cytosolic SHMT4 (AT4g13930) and SHMT5 (AT4g13890), in addition to the nucleic members SHMT6 (AT1g22020) and SHMT7 (AT1G36370). Glyma: G. max; Vitvi: V. Vinifera; Carpa: C. papaya; Arath: A. thaliana; Medtr: M. truncatula; Poptr: P. trichocarpa; Sorbi: S. bicolor; Orysa: O. sativa; Selmo: S. moellendorfii; Phypa: P. patens; Chlre: C. reinhardtii. (B) One SHMT subunit with highlighted catalytic sites, PLP and THF cofactor binding and oligomeric structural residues labelled. Domain variation analysis of the GmSHMT classes showing that most of the domain variation was observed within the nucleic-targeted GmSHMT class, with 14 domain variation out of 40, affecting protein structure (dimerization and tetramerization), substrate binding (including THF and PLP binding), and catalysis. NI: Transcripts Non-Induced under SCN infection; IRL: Transcripts Induced in Resistant line only under SCN infection; IRSL: Transcripts Induced in Resistant and Susceptible lines under SCN infection.