Figure 4.
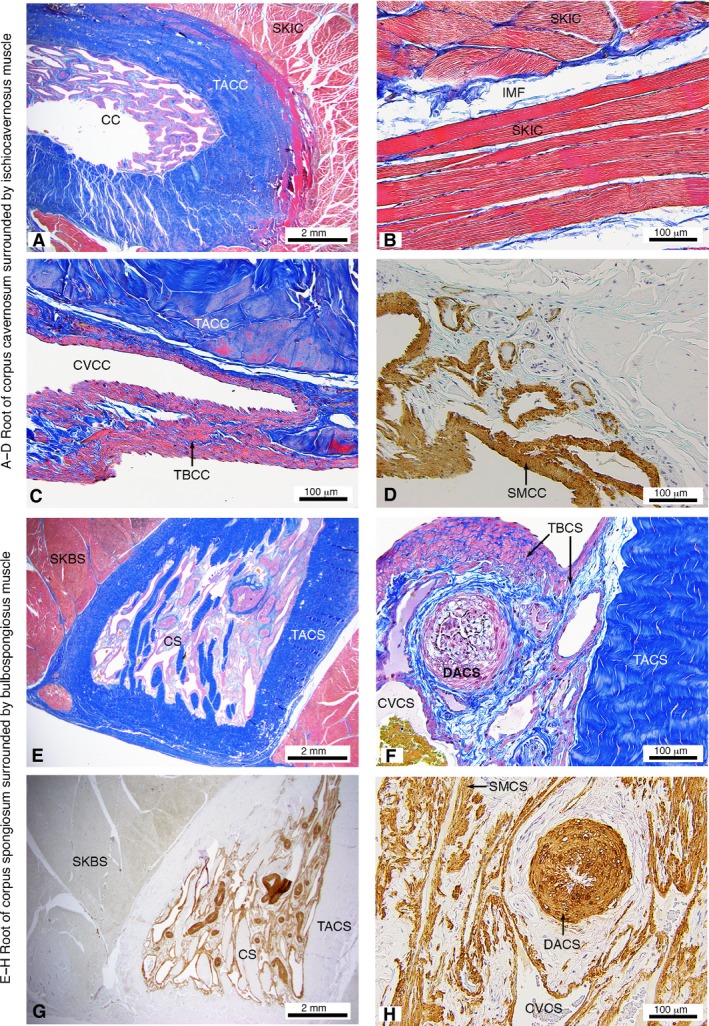
Histological appearance of the M. ischiocavernosus surrounding the root of the corpus cavernosum (A–D) and M. bulbospongiosus surrounding the root of the corpus spongiosum (E–H) of the western grey kangaroo Macropus fuliginosus (longitudinal sections). Martius Scarlet Blue highlighting collagen (blue) and muscle (red) (A–C,E–F) and Smooth Muscle Actin (D,G–H). CC, corpus cavernosum; CS, corpus spongiosum; CVCC, cavernous veins of corpus cavernosum; CVCS, cavernous veins of corpus spongiosum; DACS, deep artery of corpus spongiosum; IMF, intramuscular fascia; SKBS, skeletal muscle fibres of the M. bulbospongiosus; SKIC, skeletal muscle fibres of the M. ischiocavernosus; SMCC, smooth muscle in trabeculae of corpus cavernosum; SMCS, smooth muscle in trabeculae of corpus spongiosum; TACC, tunica albuginea of corpus cavernosum; TACS, tunica albuginea of corpus spongiosum; TBCC, trabecular of the corpus cavernosum; TBCS, trabecular of the corpus spongiosum.
