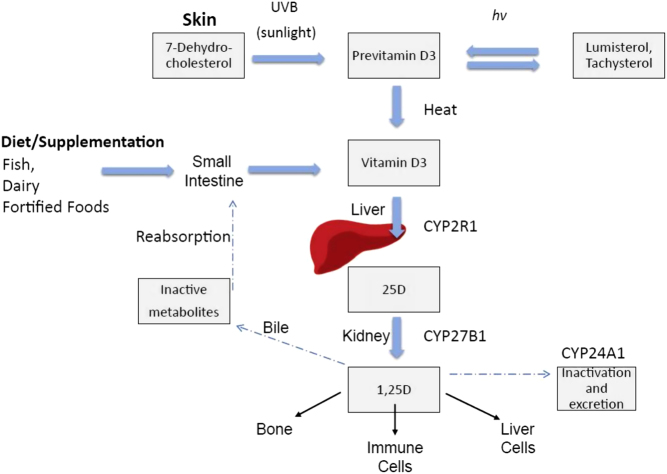
Figure 1.
Vitamin D endogenous synthesis and metabolism. Endogenous vitamin D synthesis occurs primarily through sunlight exposure which produces pre-vitamin D3. It is hydroxylated in the liver and then in the kidney, producing 1,25D (1,25 dihydroxyvitamin D), the physiologically active form of vitamin D which acts in target sites in bone and immune cells, as well as liver cells. Abbreviations: CYP (cytochrome P450), UV-B (ultraviolet-B), hν (denotes photochemical reaction). Reproduced from Keane et al. (14) under the terms of the CC Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) licence.

 This work is licensed under a
This work is licensed under a