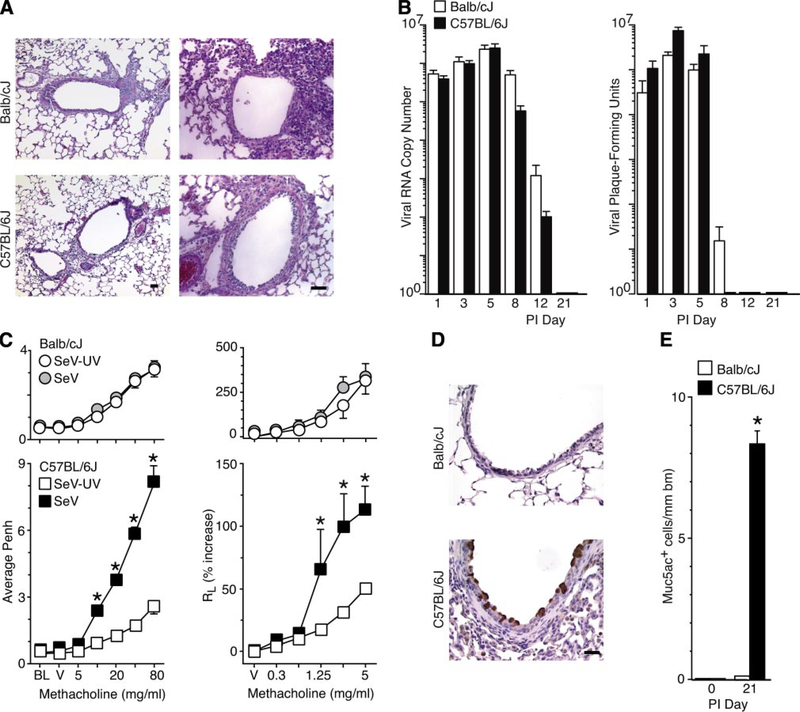
Fig. 1.
Susceptibility to virus-induced airway disease traits in inbred mouse strains. Balb/cJ and C57BL/6J mice were inoculated with Sendai virus (SeV) or an equivalent amount of UV-inactivated SeV (SeV-UV) and analyzed as follows. A: sections were subjected to hematoxylin-eosin staining at 8 days postinoculation (PI). B: lungs were used to quantify levels of viral RNA by real-time PCR and replicating virus by plaque-forming assay. C: airway reactivity to inhaled methacholine (MCH) was monitored using enhanced pause (Penh) or total lung resistance (RL) at 21 days after inoculation. Measurements are made at baseline (BL) and after exposure to vehicle (V) or MCH (5–80 mg/ml or 0.3–5 mg/ml). D: lung sections were subjected to immunostaining for mucin 5AC (Muc5ac) at 21 days after inoculation. E: quantitative analysis of immunostaining from D. All values represent means ± SE. *Significant difference between strains in B or from SeV-UV controls for C and E. Bars 20 μm.