Fig. 7.
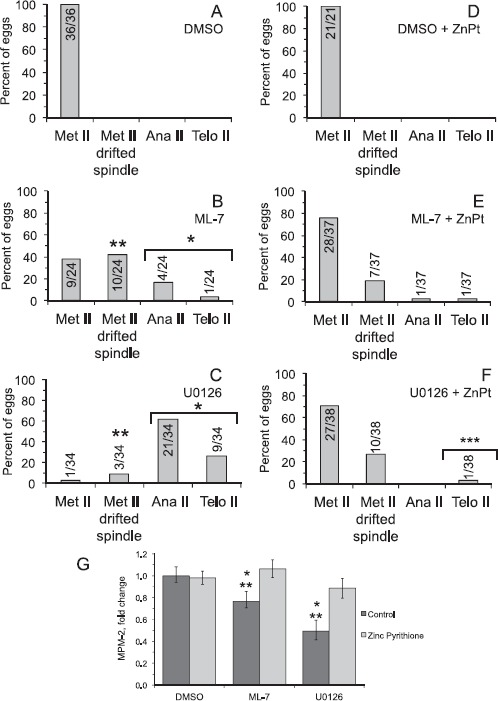
Effects of zinc ionophore treatment on U0126- and ML-7-induced parthenogenetic exit from metaphase II arrest. For D–F, metaphase II eggs were hyperloaded with zinc through treatment with 10 μM zinc pyrithione (ZnPT) for 5 min, then treated with 0.5% DMSO, 15 μM ML-7, or 50 μM U0126 for 3 h. In A–C, control eggs were not treated with ZnPT and simply treated with 0.5% DMSO, 15 μM ML-7, or 50 μM U0126 for 3 h. In A–F, eggs were analyzed and classified as in Figures 3 and 4: metaphase II, MII drifted spindle (i.e., the DNA was aligned along the metaphase II plate and the spindle was greater than 12 μm from the cortex; shown in Fig. 2), anaphase II, or telophase II (progression out of metaphase II arrest). Numbers in or above the bar indicates numbers of eggs analyzed. The number of eggs that exited from metaphase II arrest following treatment with U0126 is statistically significant compared to U0126-treated eggs that were pretreated with the ZnPT (chi-square analysis, ***P < 0.0001). Other statistical comparisons: The extent of progression out of metaphase II arrest in U0126- and ML-7-treated eggs is statistically significant as compared to DMSO-treated eggs (chi-square analysis, *P < 0.0001). The extent of drifted spindle occurrence in U0126- and ML-7-treated eggs is statistically significant as compared to DMSO-treated eggs (chi-square analysis, ***P < 0.0001). G) Quantification of MPM-2 signals in eggs in the different experimental treatment groups, either not treated with ZnPT (control, dark bars) or treated with ZnPT (light bars). Values were normalized to DMSO-treated control metaphase II eggs. Error bars represent standard error of the mean. Asterisks over the bars indicate distinct statistically significant differences (determined by ANOVA with Fisher's protected least significant different post hoc testing); one asterisk indicates statistically significantly different compared to the group in DMSO and Ca2+-containing medium, and two asterisks indicate statistically significantly different compared to the group in ZnPT-loaded eggs. Number of eggs analyzed, 21–37 per group.
