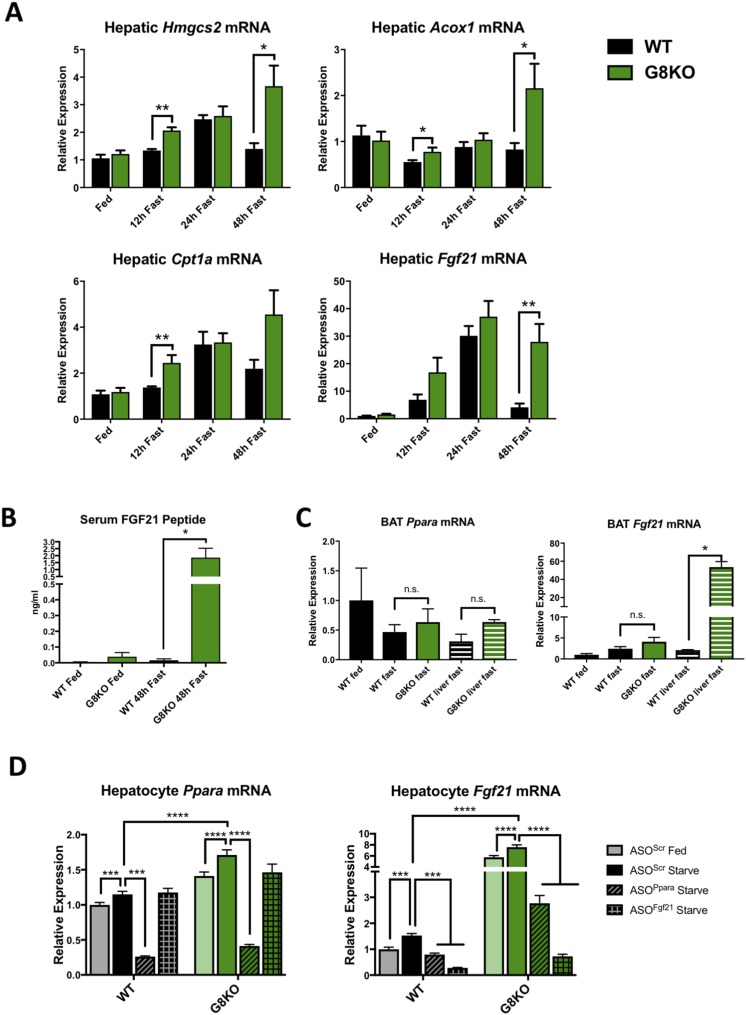
Figure 5.
Prolonged, PPARα-dependent activation of FGF21 and ketogenesis in G8KO mice. (A) qRT-PCR analysis of hepatic mRNA transcript levels of the PPARα targets Hmgcs2, Acox1, Cpt1a, and Fgf21 in WT and G8KO mice fed an ad libitum chow diet or fasted for 12, 24, and 48 hours (fed, n = 9 mice per genotype; 12-hour fast, n = 4 to 6 mice per genotype; 24-hour fast, n = 2 to 7 mice per genotype; 48-hour fast, n = 5 to 10 mice per genotype). (B) Serum FGF21 protein measurements in mice fed an ad libitum chow diet or fasted for 48 hours (n = 7 to 10 mice per group). A significant two-way analysis of variance diet-genotype interaction was detected (P < 0.05). (C) mRNA quantification of Ppara and Fgf21 in BAT from WT and G8KO fed or fasted mice, alongside WT and G8KO fasted liver tissue for comparison (WT fed, n = 2 mice per group; WT fast, n = 4 mice per group; G8KO fast, n = 5 mice per group; WT liver fast, n = 2 mice per group; G8KO liver fast, n = 2 mice per group). (D) qRT-PCR quantification of Ppara and Fgf21 in primary hepatocytes isolated from fed WT and G8KO mice. Cells were transfected with scrambled ASOs (ASOScr) or with ASOs targeting Ppara (ASOPpara) or Fgf21 (ASOFgf21) and treated with regular (fed) or starved media for 24 hours (n = 4 to 6 mice per group). Data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001. n.s., not significant.