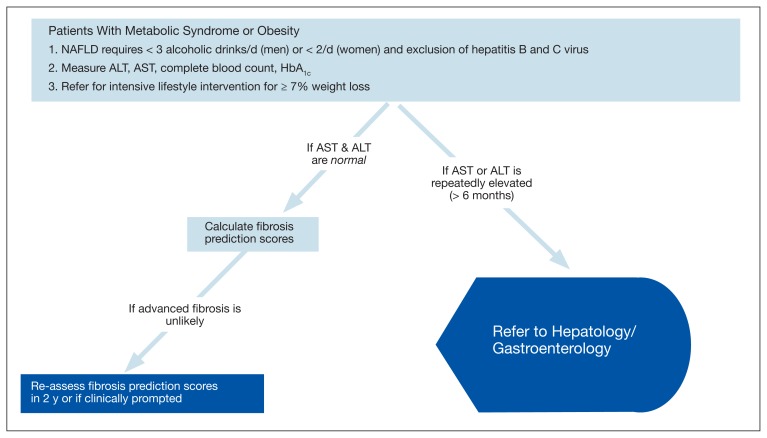
FIGURE 3.
Identification and Treatment of NAFLD in Patients With Metabolic Syndrome or Obesity
Abbreviations: ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; HbA1c, hemglobin A1c; NAFLD, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus.
In patients with metabolic syndrome or obesity with limited or no alcohol use and negative hepatitis B and C virus serology, NAFLD is evaluated with liver enzymes, complete blood count, HbA1c and calculation of fibrosis prediction scores, such as FIB-4 or NAFLD fibrosis score. All patients with likely NAFLD, metabolic syndrome, or obesity merit intensive lifestyle intervention to achieve ≥ 7% or greater weight loss to improve their fatty liver and to prevent progression to T2DM. In patients with normal liver enzymes and fibrosis prediction scores suggesting that advanced fibrosis is unlikely, the patient should be followed with liver enzymes and repeat fibrosis prediction scores to assess NAFLD progression, as well as periodic evaluation for the development of T2DM. In those with liver enzyme elevations or fibrosis prediction scores revealing probable advanced fibrosis, the patient is referred to hepatology or gastroenterology for further evaluation.