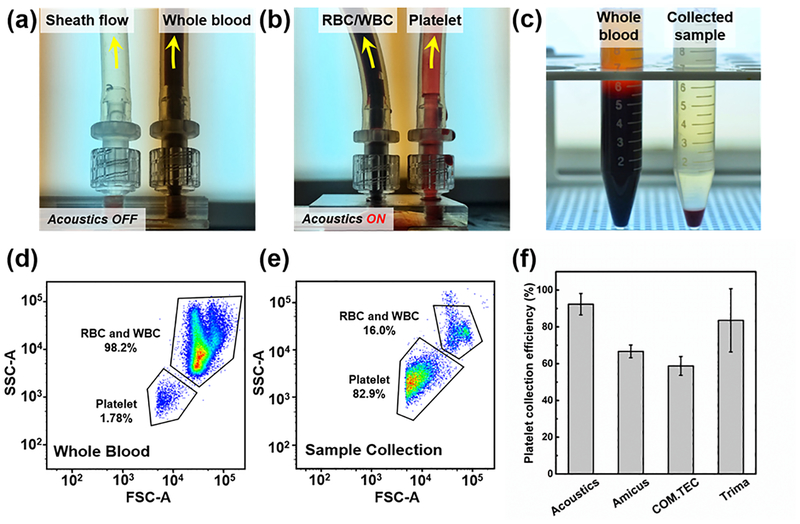
Figure 4.
(a) When the acoustic transducer is off, whole blood are collected at the right outlet; (b) when the acoustic transducer is on, RBCs/WBCs are separated to the left outlet in response to the acoustic radiation force, and therefore, the platelets are collected at the right outlet. (c) The comparison of whole blood (left) and collected platelet sample (right). The flow cytometry results using (d) the whole blood and (e) collected sample. (f) The comparison of platelet collection efficiency between our acoustic device and three commercial plateletpheresis systems (Fenwal Amicus, Fresenius COM.TEC, and Trima Accel). The data of commercial plateletpheresis systems is studied by Keklik, M. et al.36 The data represent three independent experiments as average ± standard deviation.