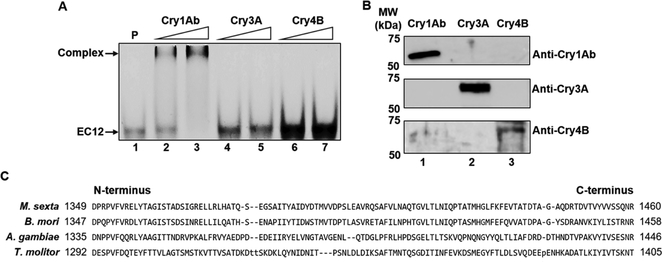
Figure 4:
Exclusive binding of CrylAb to EC12. (A) Selective binding of CrylAb to EC12, compared to the beetle toxin, Cry3A, and the mosquito toxin, Cry4B, was demonstrated by fluorescent imaging of the EC12 probe (200 nM) in the presence of Cry1Ab (lanes 2 and 3) at 100 and 200 nM, respectively, Cry3A (lanes 4 and 5) and Cry4B (lanes 6 and 7) at 200 and 400 nM, respectively. P: EC12 probe only (lane 1). (B) Western blot analysis showing specific recognition of Cry1Ab, Cry3A and Cry4B proteins with their respective antisera. Upper panel: anti-Cry1Ab; middle panel: anti-Cry3A; lower panel: anti-Cry4B. Cry1Ab, Cry3A and Cry4B samples are indicated on the image. (C) Multiple sequence alignment of the EC12 region of BT-R from M. sexta (moth, AAG37912) with Bombyx mori (moth, BAA99404), Anopheles gambiae (mosquito, AGH20077.1) and Tenebrio molitor (beetle, ABL86001.2) cadherin proteins.